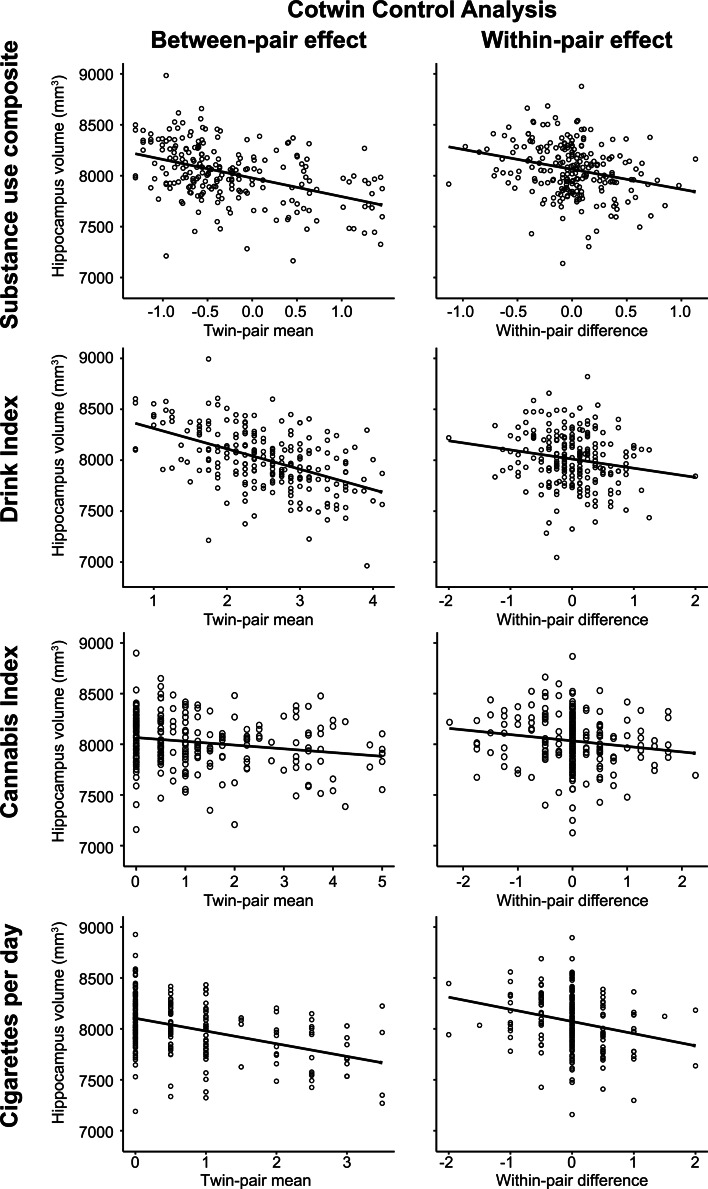
Fig. 2.
Plots depict the cotwin control analysis models of substance use on total hippocampal volume in women. Between-pair and within-pair effects are depicted with model fit lines from the linear mixed models reported in Table 3. The between-pair effect plots illustrate the significant association between lower hippocampal volume and the mean level of substance use composite, drink index, or cigarettes per day scores within a twin pair, consistent with a premorbid familial risk association. The within-pair effect plots illustrate that heavier-using twins (positive within-pair difference scores), and in particular, the heavier-drinking and heavier-smoking twins, exhibited significantly lower hippocampal volume relative to their lesser-using cotwins (negative within-pair difference scores), consistent with an exposure effect. The cannabis between-pair and within-pair effects had the expected negative association with hippocampal volume but neither effect was significant. The visreg R package (Breheny & Burchett, 2017) was used to create the partial residual plots.