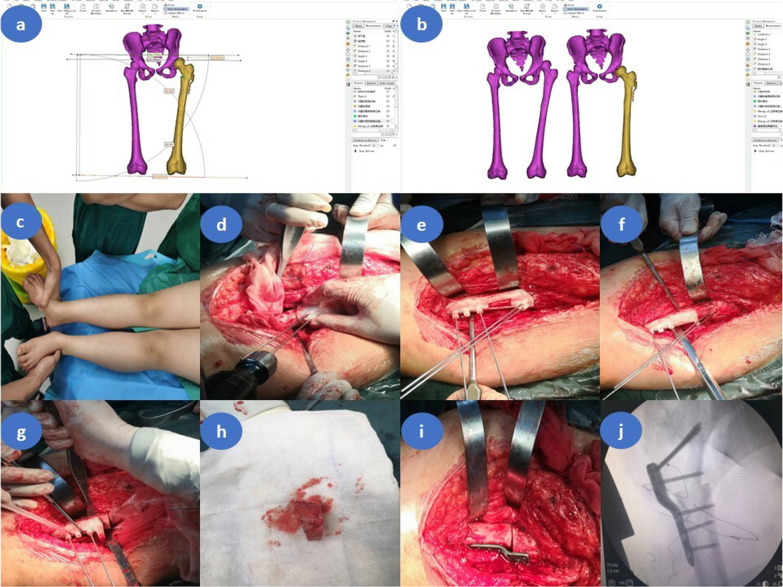
Fig. 2.
Intraoperative application of the osteotomy navigation templates in children with left developmental dysplasia of the hip (female patient, 5.5 years old, Tönnis type III). a Preoperative surgical planning in 3-Matic software. b Comparison of preoperative and postoperative CT scan three-dimensional reconstruction in 3-Matic software. c Both lower limbs are unequal, with the left shorter than the right. d Kirschner wires placement assisted by the positioning guide. e The distal Kirschner wires were properly inserted with the assistance of the connecting guide plate. f Implantation of the oblique osteotomy guide plate under the guidance of the distal Kirschner wires. The angle tilted cephalad to the osteotomy guide is the angle of varus of the proximal femur, and the first osteotomy was conducted by the swing saw with the aid of the guide. g The transverse osteotomy guide plate was placed under the guidance of distal Kirschner wires. The osteotomy surface of the guide plate was perpendicular to the femur, and the second osteotomy was conducted by the swing saw with the aid of the guide plate. The angle between the two osteotomy surfaces is the proximal femoral varus angle, and the length of the lateral femoral cortex between the two osteotomy surfaces is the additional shortening distance of the femur. h Trapezoidal bone block cutoff with the assistance of the guide plates. i LCP-PHP fixation of the distal and proximal femur. j C-arm fluoroscopy showed the plate was well-positioned and the anticipated orthopedic result was achieved