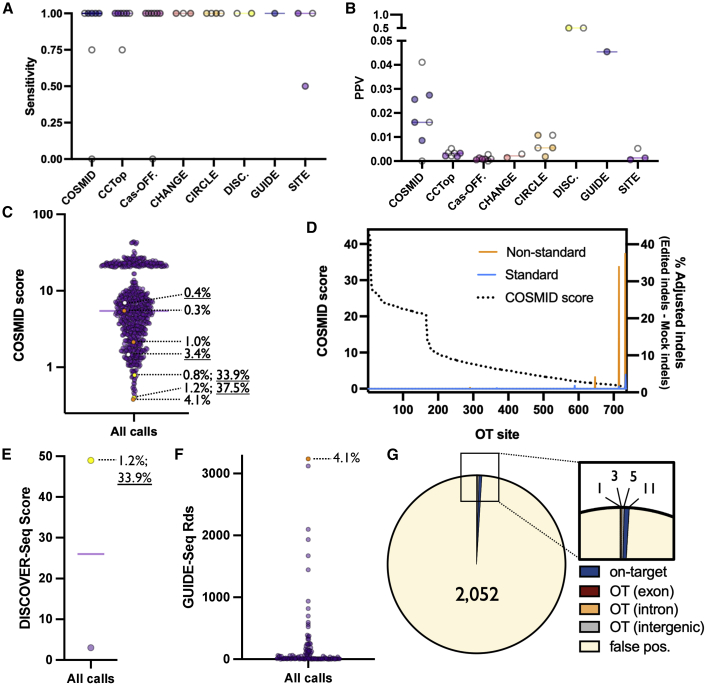
Figure 5.
Performance of OT discovery methods
(A) Each dot depicts sensitivity for each gRNA for each discovery method. White dots indicate results derived from non-standard (i.e., WT Cas9 or truncated gRNA) conditions. Note: sensitivity was unable to be calculated in treatments where no OT sites were found. (B) Each dot depicts PPV for each gRNA for each discovery method. All sites not on panel are assumed to be false positives. White dots indicate results derived from non-standard conditions. Note: PPV was not plotted for treatments where no OT sites were found. (C) Each dots depicts the COSMID score for all candidate OT sites for all gRNAs. True positives and corresponding indel frequencies are shown by dotted lines (WT indel frequency underlined). Orange, white, and yellow dots indicate OTs generated by HiFi, WT, and both HiFi and WT Cas9, respectively. (D) For each OT site—rank ordered left to right from high COSMID score to low along the x-axis—COSMID score and adjusted indel percent (Edit-Mock) is plotted in standard and non-standard treatments. (E) Each dot depicts the score assigned to a single DISCOVER-Seq OT site after editing using HBB gRNA. True positive and corresponding indel frequency is shown by dotted line (WT indel frequency underlined). The yellow dot indicates OT generated by WT and HiFi Cas9. (F) Each dot depicts the number of reads covering a single GUIDE-Seq OT site following editing with AR, CTNNB1, EMX1, FANCF, HPRT, and VEGFA gRNAs. True positive and corresponding indel frequency is shown by dotted line. The orange dot indicates OT generated by HiFi Cas9. (G) Pie chart summarizing proportion of on-target, OT, and false positives across all treatments for sites achieving sufficient coverage depth. False positives are defined as putative OT sites on panel that met coverage threshold that were not found to have OT activity.