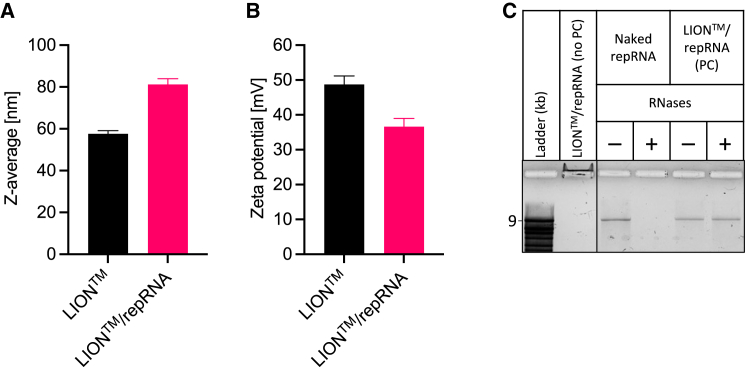
Figure 13.
Physicochemical characteristics of LION formulation and LION/repRNA complexed vaccine
Mean (±SD) (A) z-average particle size and (B) zeta potential characteristics before and after mixing LION and repRNA to form LION/repRNA complex at N:P ratio of 15. (C) Denaturing agarose gel electrophoresis was performed to assess binding of repRNA with LION, shown in lane labeled “LION™/repRNA complex (no PC),” where PC denotes phenol-chloroform extraction. As observed, no free repRNA was detected, and bound repRNA migrated toward the negatively charged electrode due to the net positive charge of the LION/repRNA complex. Also shown is the role of LION in repRNA protection against RNase-catalyzed hydrolysis. Naked (unformulated) repRNA or LION/repRNA complex was incubated in nuclease-free water (−) or RNases (+), followed by proteinase K inhibition and extraction with phenol-chloroform (PC). Compared with naked repRNA, LION-formulated repRNA was protected from RNases. All samples were run on the same gel.