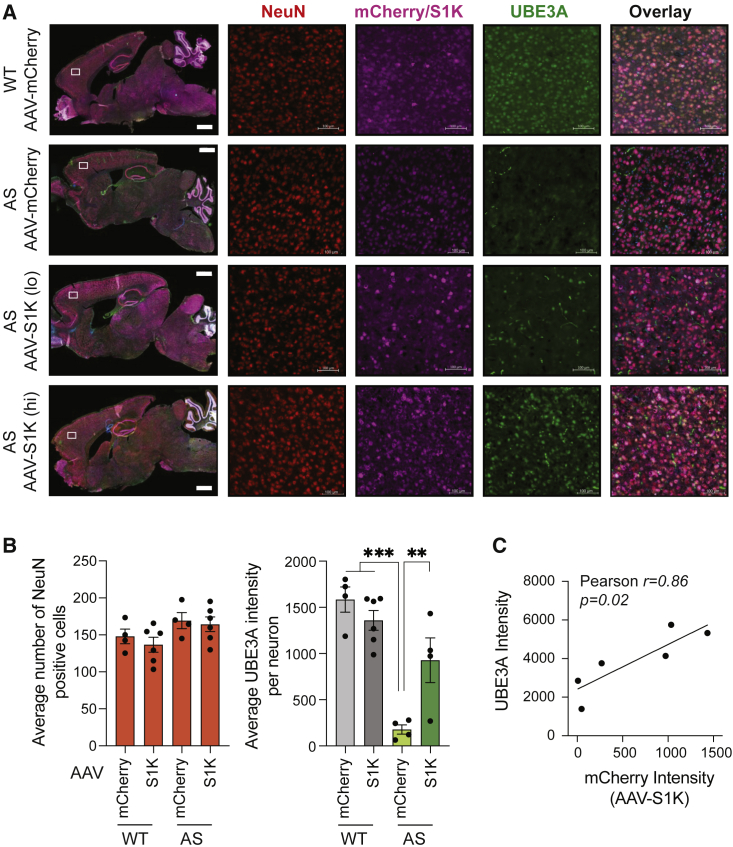
Figure 4.
Brain-wide and dose-dependent restoration of UBE3A in mature neurons
(A) Immunostaining of sagittal brain sections (scale bar, 1,000 μm) including cortex isolated regions (scale bar, 100 μm) was performed 5 weeks after AAV-S1K treatment. Mice were evaluated at 11 weeks of age. Representatives are shown for WT (top row), AS mice (second row), and AAV-S1K-treated AS mice (bottom two rows). AS mice with low mCherry intensity are labeled AAV-S1K (lo), while AS mice with mid to high mCherry intensity are labeled AAV-S1K (hi). Brain tissue was labeled for mature neurons (NeuN+, red), ATF-S1K (mCherry+, violet) and UBE3A (green). Merged images are shown for the sagittal section and the cortex region (last column). Zoom-in images are shown in Figure S5. (B) Number of NeuN-positive cells is comparable across different genotypes (AS, WT) and treatments (AAV-mCherry, AAV-S1K). Restoration of UBE3A was quantified by UBE3A intensity analysis in NeuN+/mCherry+ neurons in the prefrontal cortex after AAV-S1K treatment in AS mice and control groups (n ≥ 4, mean ± SEM, one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 ∗∗p < 0.01). (C) Dose-dependent UBE3A increase was identified by correlation analysis of UBE3A and mCherry intensities in NeuN+/mCherry+ neurons (Pearson correlation, ∗p < 0.05).