Fig. 2.
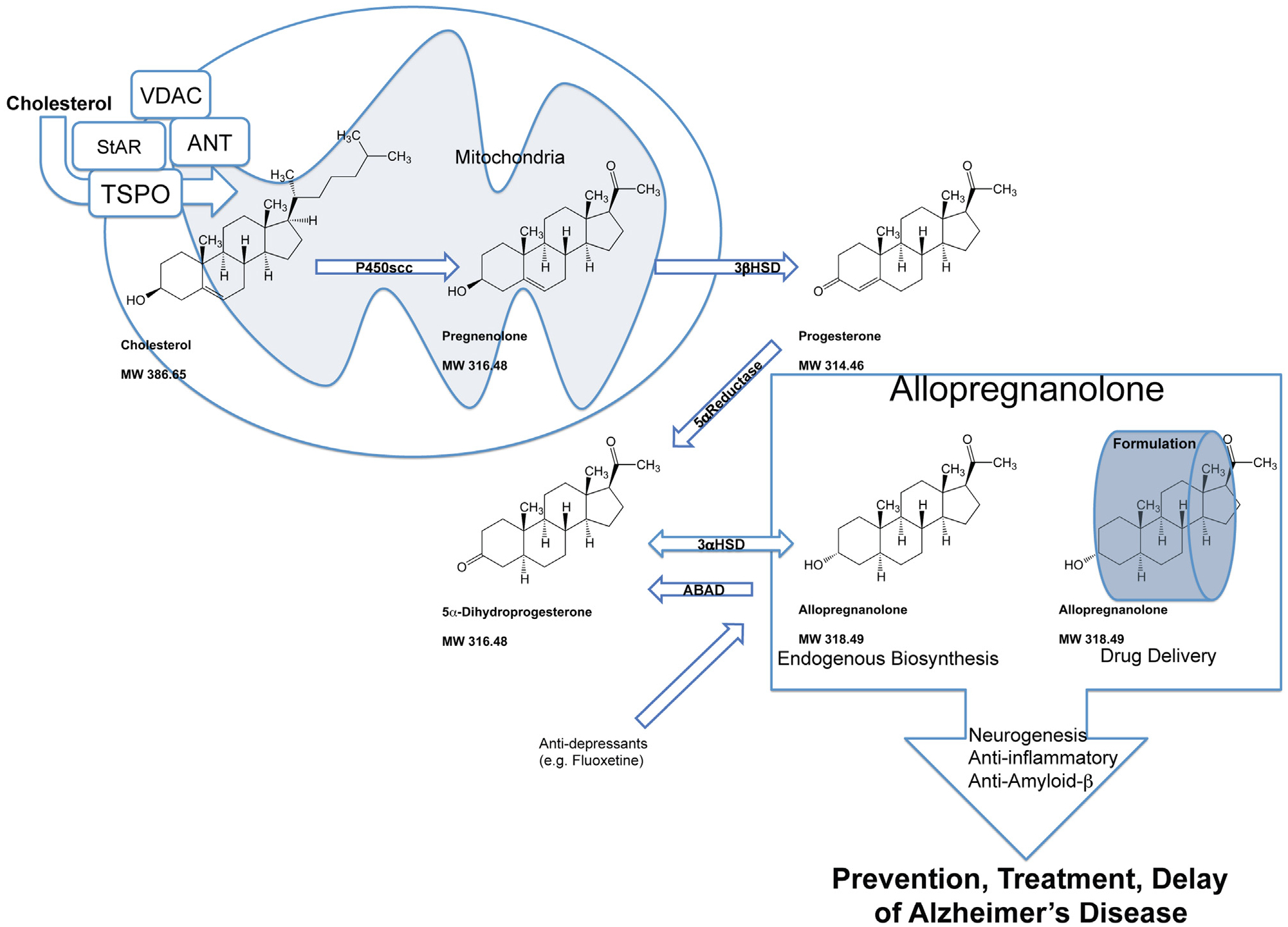
Neurosteroid biosynthesis is a multi-step enzymatic pathway. Cholesterol homeostasis, recruitment to the mitochondrial compartment, enzymatic reduction and transport to neural and glial cells or their precursor cells require regulation of multiple mechanisms critical to Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Allo mechanisms of action promote neurogenesis, oligodendrogenesis, and on a systems-level inhibit excess inflammation and β-amyloidogenesis. In the central and peripheral nervous systems, neurosteroid synthesis occurs in myelinating glial cells, astrocytes, and several neuronal cell types including neural progenitors. Cholesterol is supplied to these cell types and presented to the mitochondria. The mitochondrial membrane translocator protein (TSPO) controls the uptake of cholesterol and the synthesis of neuroactive steroids (Rupprecht et al., 2010). TSPO-associated proteins form a cholesterol transport pore in the mitochondrial inner membrane that include the steroidogenic acute regulatory protein (StAR), voltage-dependent anion channel protein (VDAC), and adenine nucleotide transporter protein (ANT). The mitochondrial pore transports cholesterol to the mitochondrial matrix to be converted into pregnenolone by the cytochrome P450 side-chain cleavage (CYP450scc) enzyme (Liu et al., 2006). Pregnenolone diffuses to the cytosol and then is converted to progesterone by the 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3β-HSD) enzyme. Peripherally derived progesterone and Allo cross the blood-brain barrier to also contribute to the neurosteroid concentration. Allo is synthesized from progesterone in two enzymatic steps by 5α-reductase (5α-R) type-I and 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (3α-HSD) in the brain de novo (Mellon, 2007; Mellon et al., 2001). The rate-limiting step in neurosteroidogenesis is the reduction of progesterone to 5α-dihydroprogesterone (5α-DHP) by 5α-R. Subsequently, 3α-HSD catalyzes conversion of 5α-DHP into Allo. Amyloid beta-binding alcohol dehydrogenase or (also known as ABAD; SCHAD; 17βHSD10) is an enzyme that associates with mitochondria and facilitates back conversion of Allo to 5α-DHP (He et al., 2005; Yang et al., 2005). Additionally, anti-depressants such as fluoxetine are pro-neurogenic and have been shown to increase Allo production in the brain (Malberg et al., 2000; Uzunova et al., 2004, 2006). Endogenous Allo or optimal therapeutic dose of Allo with proper drug delivery strategy promote neurogenesis, oligodendrogenesis, and on a systems-level inhibit excess inflammation and β-amyloidogenesis.
