Fig. 3.
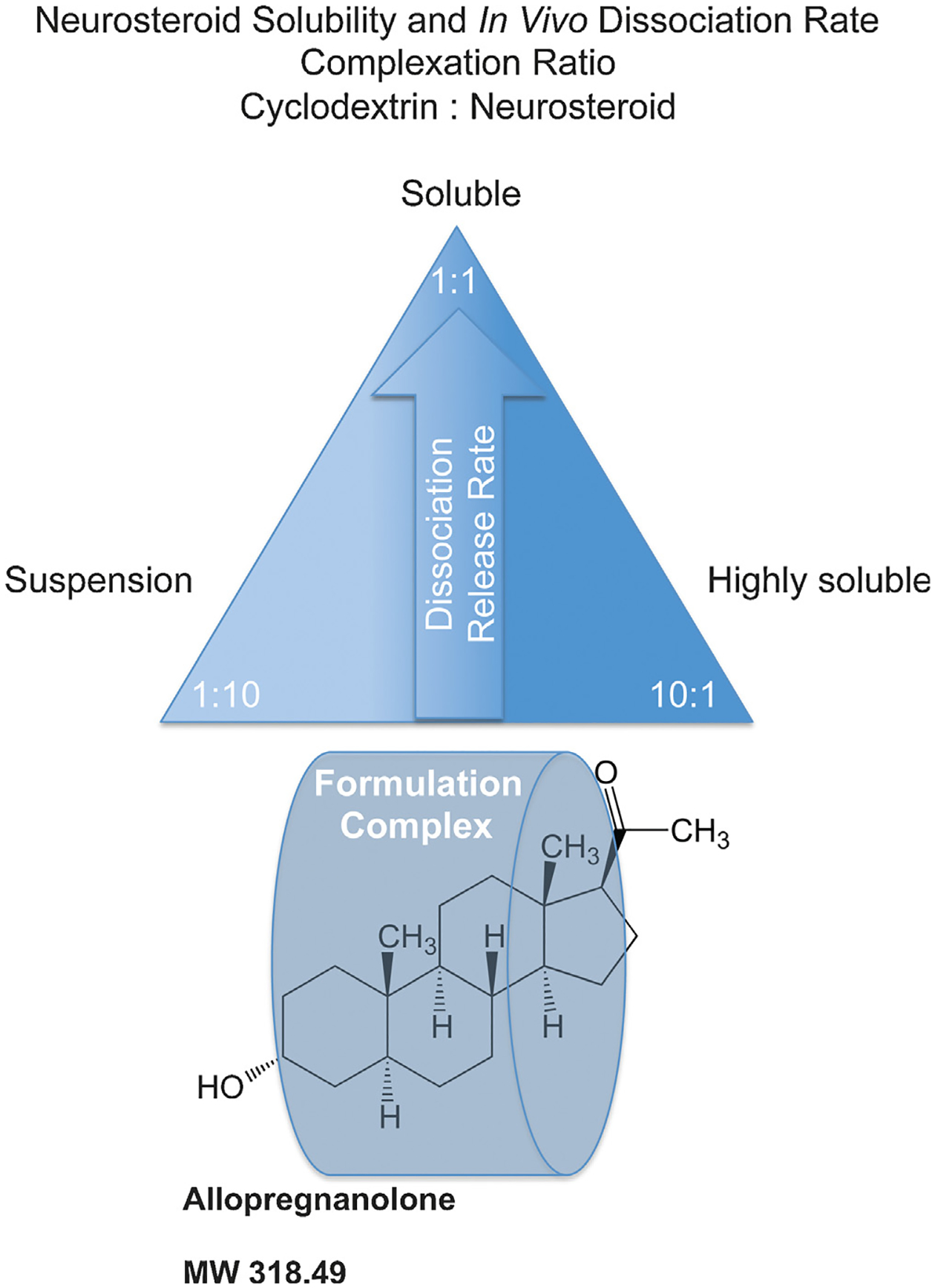
The neurosteroid release rate pyramid describes the relationship between release rate of active neurosteroid and aqueous cyclodextrin vehicle. Molar complexation ratios greatly alter the release rate or dissolution profile of neurosteroids including allopregnanolone (Allo) as illustrated by the release rate pyramid. Typical cyclodextrin carrier formulations utilize the cyclodextrin such as hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin, at 5–30% in aqueous solution such as water or normal saline with a maximal achievable cyclodextrin concentration between 45–60% weight to volume. Generally, a 1:1 stoichiometry inclusion complex of neurosteroid and a cyclodextrin exists at the apex of the pyramid hypothetically set at a threshold dose that requires maximal delivery rate of the neurosteroid. For Allo, the molar complexation ratio (suitable cyclodextrin:Allo) that is optimal for release rate is closer to 1:2. The same Allo dose would exhibit a slower release rate with a cyclodextrin:Allo of 1:10 complexation ratio since most of the Allo would be suspended in a depot formulation and less accessible for release and absorption into the biological system. Likewise, a complexation ratio that possesses cyclodextrin:Allo of 10:1 at the same dose of Allo would be readily soluble in an aqueous environment similar to the 1:10 suspension formulation that sits on the opposite side of the solubility spectrum. The 10:1 formulation would also be less accessible for absorption compared to the 1:1 formulation as the Allo is held within the overly abundant empty cyclodextrin molecules governed by the binding and dissociation rate. We hypothesize that the 10:1 formulation displays a re-uptake phenomenon whereby the neurosteroid is relatively less likely to be released into the biological system and therefore slower to release and interact with the receptor targets. A desired pharmacokinetic profile can be titrated by understanding the complexation ratio and release rate to optimize a measurable biological effect such as neurogenesis, anxiolytic activity, or sedation. For Allo, ataxia or sedation can be used as a measurable biomarker of target engagement and can establish the maximally tolerated dose in relation to formulation and delivery route. The lowest possible dose to experience sedation for example at 1:1 formulation would elicit little or no effect with 1:10 or 10:1 formulation complexes.
