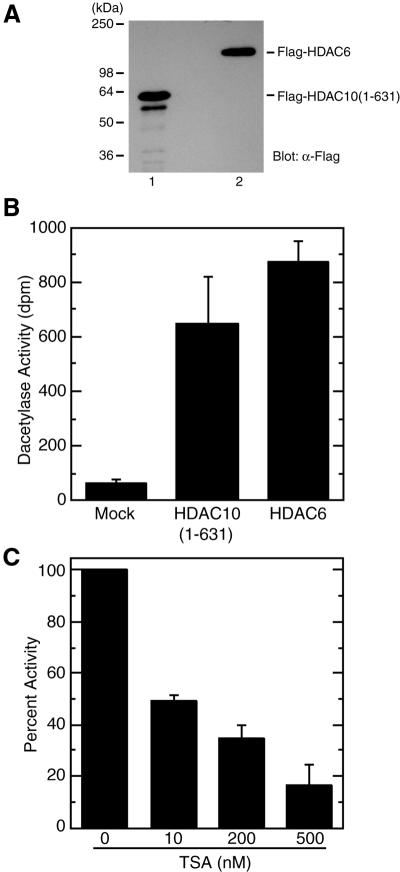
Figure 3.
Deacetylase activity of HDAC10. (A) Expression of HDAC10 from Sf9 cells. HDAC10(1–631) was expressed in Sf9 cells as a Flag-tagged fusion protein. This fusion protein was then immunoprecipitated on anti-Flag M2 agarose, washed extensively with buffer B containing 0.5 M KCl and eluted with buffer B containing 0.15 KCl supplemented with Flag peptide. For comparison, Flag-HDAC6 was similarly expressed and affinity purified. Eluted proteins were analyzed by western blotting with anti-Flag antibody. (B) Deacetylase activity of Flag-HDAC10 and Flag-HDAC6. Equivalent amounts of Flag-HDAC10(1–631) and Flag-HDAC6 were used for deacetylating [3H]acetylhistones and the release of [3H]acetate (d.p.m.) from [3H]acetylhistones was quantified as deacetylase activity. As a control, extracts from uninfected Sf9 cells were subjected to similar purification. Flag-HDAC6 proteins expressed in and affinity purified from Sf9 and 293 cells were found to possess similar deacetylase activity (N.R.Bertos and X.-J.Yang, unpublished data). Average values from three independent experiments are shown with standard deviations. (C) Effect of TSA on the deacetylase activity of HDAC10(1–631). Deacetylase assays were carried out in the presence of the indicated TSA concentrations. The release of [3H]acetate in the absence of TSA was set to 100%. Average values from three independent experiments are shown with standard deviations.