Figure 5.
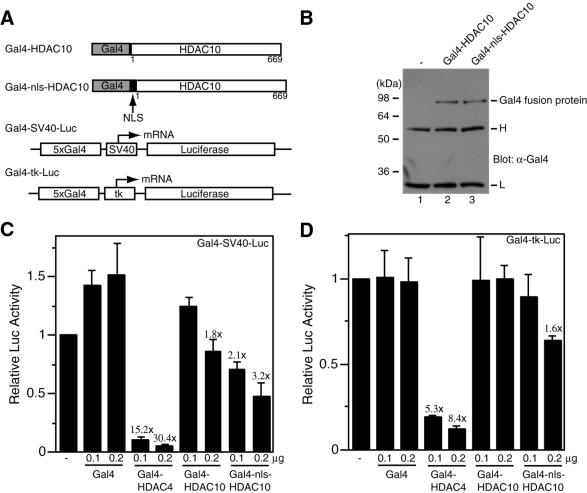
Transcriptional repression by tethered HDAC10. (A) Schematic representation of Gal4 fusion proteins (Gal4–HDAC10 and Gal4–nls–HDAC10) and luciferase reporters (Gal4–SV40–Luc and Gal4–tk–Luc). NLS, nuclear localization signal; 5×Gal4, five copies of the Gal4-binding site; tk, thymidine kinase core promoter. (B) Expression of Gal4–HDAC4 and Gal4–nls–HDAC10. Extracts (10 µg/lane), prepared from 293 cells transfected with expression plasmids for the indicated fusion proteins, were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Gal4 antibody (RK5C1; Santa Cruz Biotechnology) and western blotting analysis with the same antibody. Lane 1, similar immunoprecipitation with extracts from non-transfected cells. Molecular size markers are shown at left. H, IgG heavy chain; L, IgG light chain. (C and D) Transcriptional repression by Gal4–HDAC10 and Gal4–nls–HDAC10. Mammalian constructs expressing HDAC4 and HDAC10 fused to the C-terminus of Gal4(1–147) were transfected into 293 cells along with the reporter Gal4–SV40–Luc (C) or Gal4–tk–Luc (D). Note that expression of Gal4 fusion proteins is under the control of an SV40 promoter. Luciferase activities were normalized to the internal β-galactosidase control; the normalized luciferase activity from the transfection without any effector plasmid was arbitrarily set to 1.0. Average values from three independent experiments are shown with standard deviations. The different repression abilities of Gal4–HDAC4 and Gal4–HDAC10 fusion proteins may be due to their distinct expression levels, since Gal4–HDAC4 was expressed to a much higher level (data not shown).