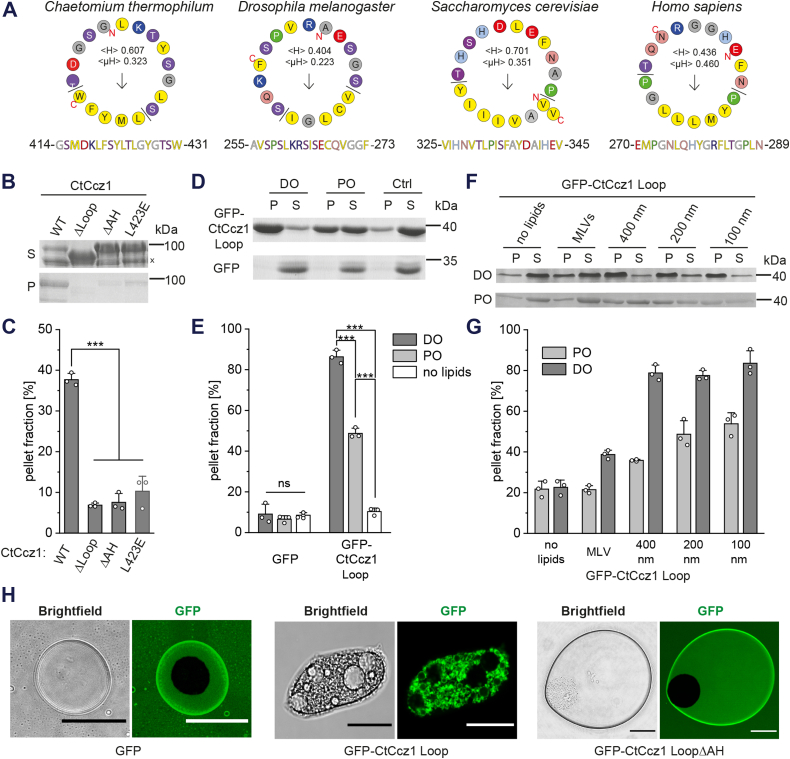
Figure 6.
Interaction of the MC1 amphipathic helix with lipids.A, helical wheel projection of the putative amphipathic helix from different model organisms (27). B, sedimentation assays of full-length CtCcz1WT or CtCcz1 variants. Liposomes were generated from a DO lipid mix. A Ccz1 degradation band is marked (x). C, quantification of B (n = 3). D, sedimentation assays of GFP-CtCcz1Loop and GFP with liposomes generated from a PO and DO lipid mix. E, quantification of D (n = 3). F, sedimentation assays of GFP-CtCcz1Loop with multilamellar vesicles (MLVs) or liposomes with a defined diameter generated from a PO and DO lipid mix. G, quantification of F (n = 4). H, oil droplets were incubated with GFP, GFP-CtCcz1Loop, or GFP-CtCcz1LoopΔAH variants and visualized by confocal fluorescence microcopy. Scale bar: 20 μm. Quantification data are presented as mean ± SD, and the significance was calculated using Student’s t test (∗∗∗p < 0.001, n.s. not significant). DO, di-oleoyl; MC1, Mon1-Ccz1; PO, palmitoyl (16:0)—oleoyl (18:1).