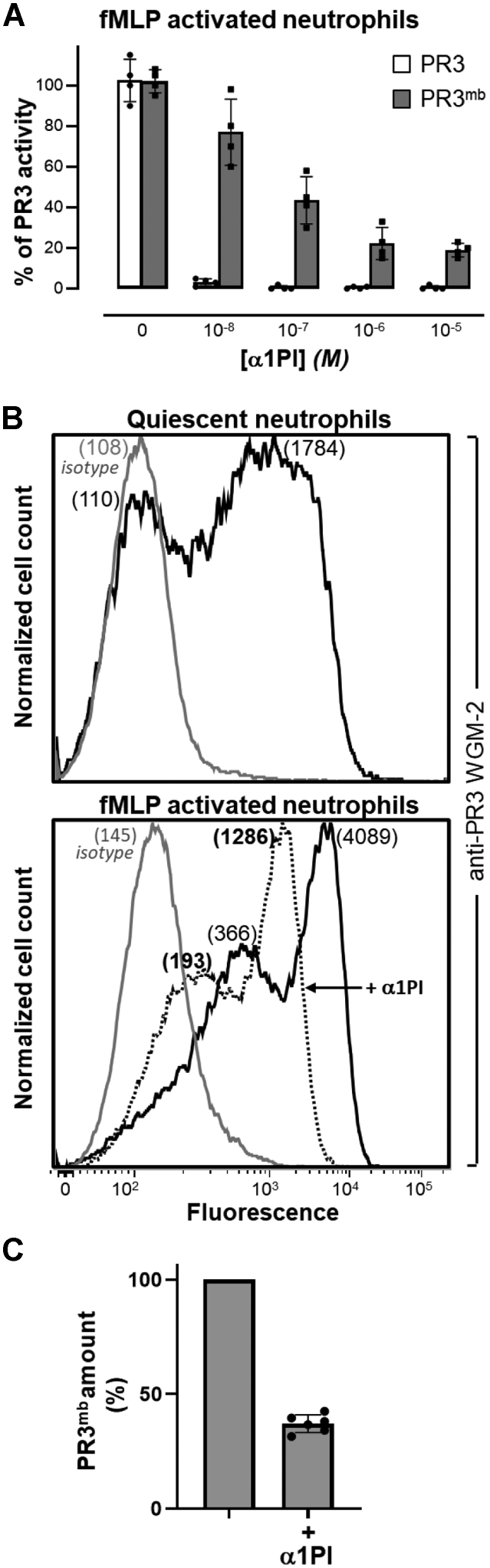
Figure 3.
Inhibition and surface exposition of PR3 on fMLP-activated neutrophils treated with α1PI.A, residual activity of soluble PR3 (gray bars) and PR3mb (black bars) after incubation with increasing amounts of α1PI (0.01–10 μM). Neutrophils were primed with CB (10 μg/ml) for 10 min and stimulated with chemotactic N-formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine (fMLP, 1 μM) for 20 min at 37 °C and the activity of PR3mb was measured using FRET substrate ABZ-VAD(nor)VADYQ-EDDnp (20 μM) (43, 57) after incubation with increasing amounts of α1PI in comparison with that of soluble purified PR3. The starting rates of hydrolysis were adjusted on that of a 1 nM PR3 solution. Individuals results and the means ± SD are given (n = 4 independents experiments). B, representative flow cytometry analysis of fMLP-activated neutrophils as analyzed using anti-PR3 WGM-2 (25 μg/ml) showing a partial decrease of the load in PR3mb after incubation with α1PI (50 μM). The proportion of PR3mb over the total neutrophil population remained unchanged. The gray line represents nonspecific binding of mouse isotype-specific IgG control antibody used at the same concentration. C, PR3mb amount on fMLP-activated neutrophils after α1PI treatment by flow cytometry (n = 5 independents experiments, See Fig. S2). Individuals results and the means ± SD are given. α1PI, alpha-1 protease inhibitor; fMLP, formyl-methionyl-leucyl-phenylalanine; PR3, proteinase 3.