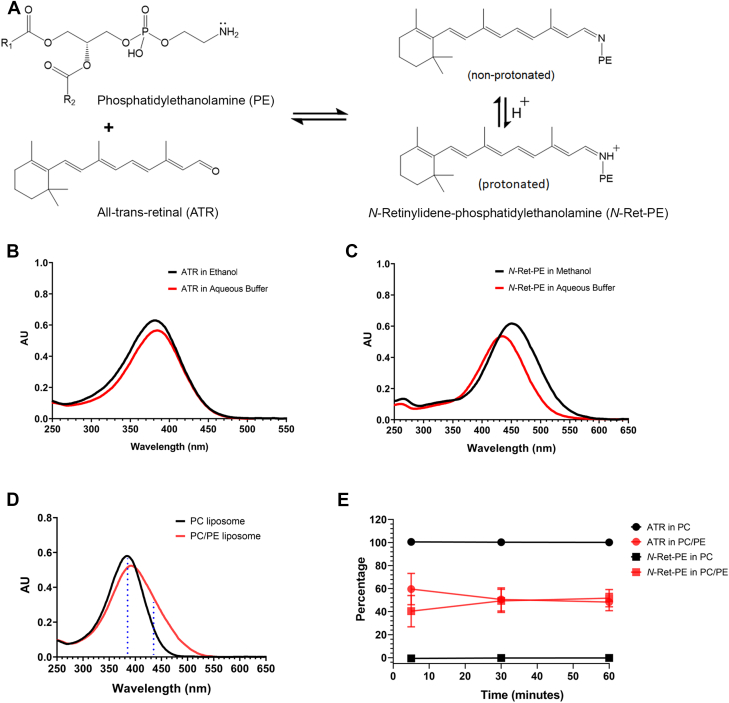
Figure 1.
Spectral characterization of all-trans retinal and N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (N-Ret-PE).A, reversible reaction of all-trans retinal (ATR) with phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) to form a mixture of nonprotonated and protonated N-Ret-PE. B, spectra of ATR in ethanol (λmax = 383 nm) and in aqueous buffer (acidified with TFA, 0.09 M Hepes Buffer pH 7.2, 0.9% CHAPS (w/v), 1.3% TFA (v/v)) (λmax = 385 nm). C, spectra of protonated N-Ret-PE in methanol acidified with 0.1% TFA (λmax = 450 nm) and in aqueous buffer (acidified with TFA) as above (λmax = 435 nm). D, representative spectra of ATR (20 μM) added to PC liposomes composed of 100% DOPC (57 μM) and PE/PC liposomes composed of 35% DOPE/65% DOPC (20 μM DOPE/37 μM DOPC) after 5 min. Dotted blue lines indicate wavelengths (385 nm and 435 nm) used to determine the percentages of ATR and N-Ret-PE at the endpoint. E, percentage of remaining ATR or N-Ret-PE formed over the sum of both determined after ATR was added to PC or PE/PC liposomes at 5 min, 30 min, or 60 min. Data represent mean ± S.D. (n = 3). CHAPS, 3-[(3-cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate; DOPC, 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; DOPE, 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; TFA, trifluoroacetic acid.