Figure 1.
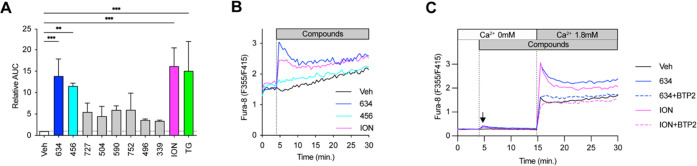
Compound 634 increases intracellular Ca2+ levels in mBMDCs. (A) Intracellular Ca2+ influx levels of the top eight compounds. THP-1 cells were loaded with the ratiometric Ca2+ indicator, Fura-2, and treated with ION (1 μM), TG (1 μM), or test compounds (5 μM). The time–response pattern of intracellular Ca2+ levels was recorded for 25 min. Area under the curve (AUC) of OD340/380 ratios corresponds to the intracellular Ca2+ kinetics, and the baseline-subtracted AUC was calculated by GraphPad Prism. Data presented are relative AUC to Veh (1.74 at 1st exp. and 1.06 ± 0.05 at 2nd exp. were set as 1, respectively) and mean ± SD of pooled data from three experiments showing similar results. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s posthoc test compared to Veh. (B) Ca2+ mobilization by compounds 456 and 634 in mBMDCs. mBMDCs were loaded with Fura-8 and treated with ION (1 μM), 634 or 456 (10 μM) for 25 min. The dashed line indicates the timing of compounds added. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments showing similar results. (C) Ca2+ add-back assay. Fura-8-loaded mBMDC were treated with ION, compound 634, ION plus BTP2, or 634 plus BTP2 for 10 min in the absence of extracellular Ca2+, and then Ca2+ (final 1.8 mM) was added. ION, 634, and BTP2 were added at final concentrations of 1, 10, and 5 μM, respectively. The data presented are averages of duplicates and representatives of two independent experiments showing similar results.