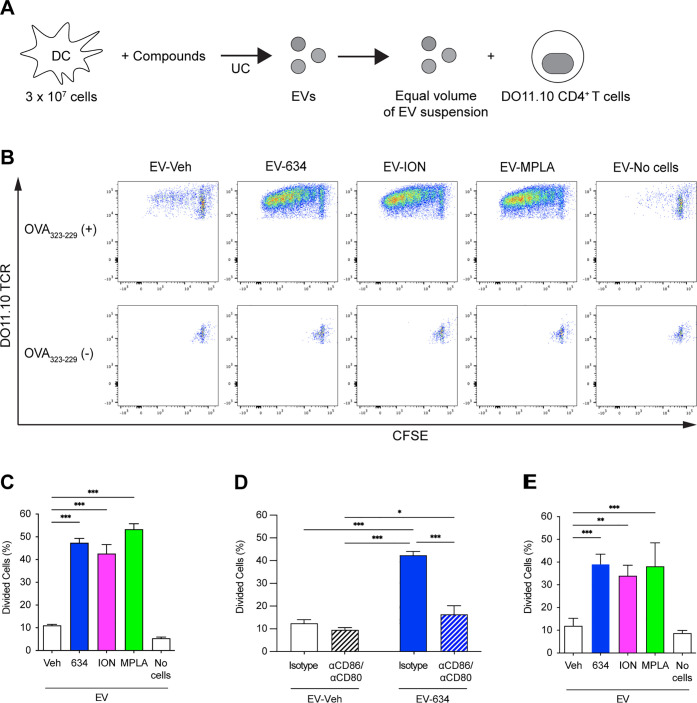
Figure 4.
EV634 enhances T cell proliferation in the presence of antigenic peptides. (A, B) CFSE-labeled CD4+ T cells isolated from splenocytes of OVA TCR transgenic strain, DO11.10; splenocytes were treated with an equal volume (7 μL out of 50 μL) of the suspensions of EVVeh, EV634, EVION, or EVMPLA in the presence or absence of OVA323-339 peptide for 5 days. EVNo cells were used as a negative control. (C–E) T cell proliferation was determined by CFSE dilution using flow cytometry. Percentages of divided T cells induced by EVs from the same volumes of the culture supernatants and the number of parent cells. Data shown are means ± SDs of triplicates representative of two independent experiments. (C) In the presence of the OVA323–339 peptide, T cells were treated with an equal volume of the EV suspensions (7 μL out of 50 μL). (D) In the presence of the OVA323-339 peptide, T cells were treated with an equal volume (7 μL out of 50 μL) of the suspensions of EVveh or EV634 in the presence of anti-CD86 and anti-CD80 antibodies or isotype controls for 5 days. Data shown are means ± SDs of triplicates representative of two independent experiments. (E) In the presence of the OVA323–339 peptide, T cells were treated with an equal particle number (3.13 × 109). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001 by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s posthoc test vs EVVeh (C and E), and by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s posthoc test (D).