Figure 2.
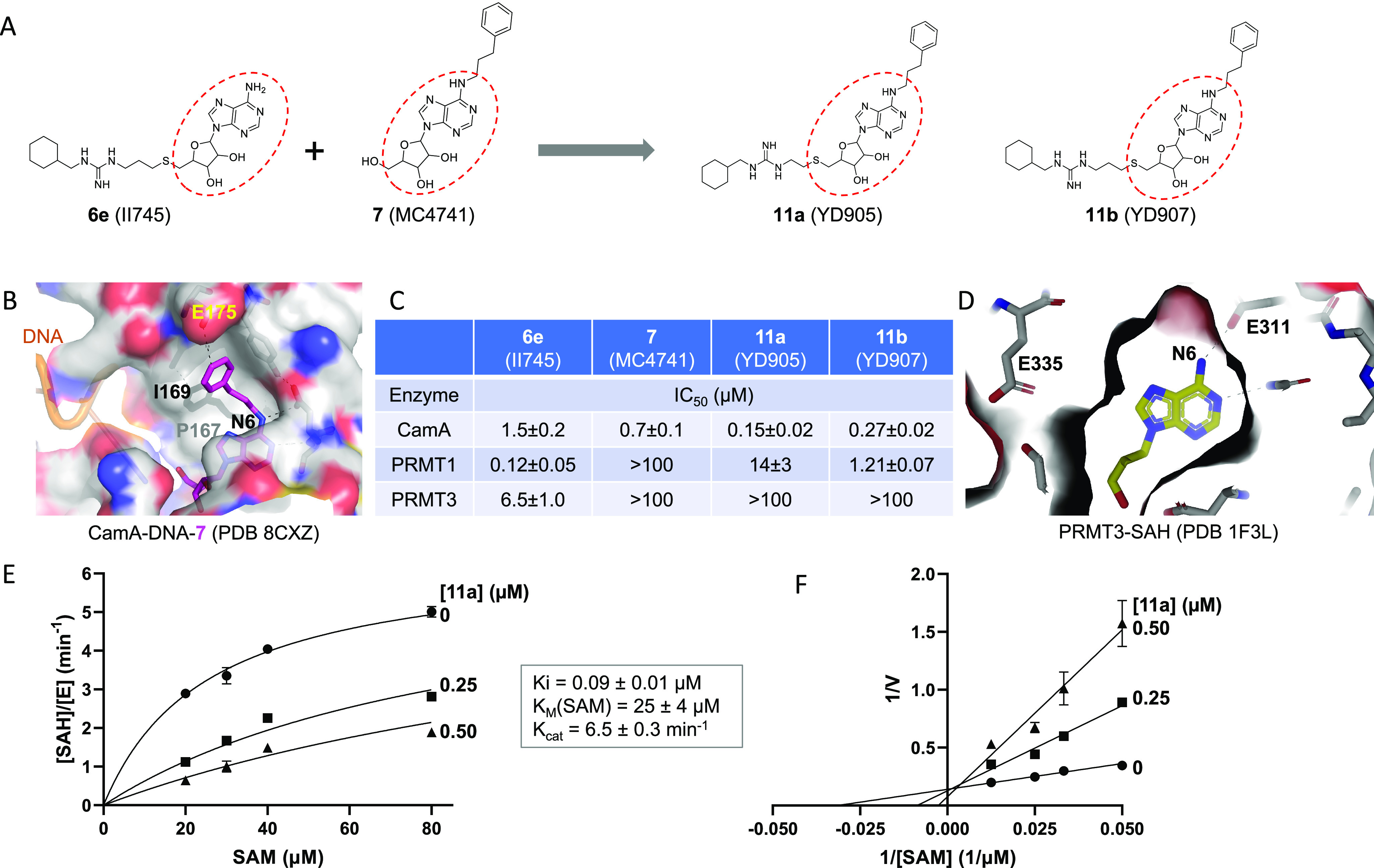
Compound 11a (YD905) is competitive with SAM. (A) Chemical structures of 6e (II745), 7 (MC4741), 11a (YD905), and 11b (YD907). 11a and 11b differ in the length of the linker (2C vs 3C) off of the sulfur atom. (B) Structure of CamA–DNA in complex with compound 7 (magenta) (PDB 8CXZ). The 3-phenylpropyl moiety at the N6-amino of adenosine is bound to a largely hydrophobic surface (colored in gray). (C) Summary of inhibition (IC50 values) of CamA, PRMT1, and PRMT3 by the four compounds shown in panel A (see Figure S1 in Supporting Information). (D) Structure of PRMT3 in complex with SAH (yellow), which is completely enclosed by PRMT3 residues (PDB 1F3L). (E) Michaelis–Menten saturation curves of CamA kinetics varying SAM concentrations (20, 30, 40, and 80 μM) and inhibitor 11a concentrations (0, 0.25, and 0.5 μM). (F) Lineweaver–Burk double reciprocal plot suggests competitive inhibition by 11a with respect to SAM.
