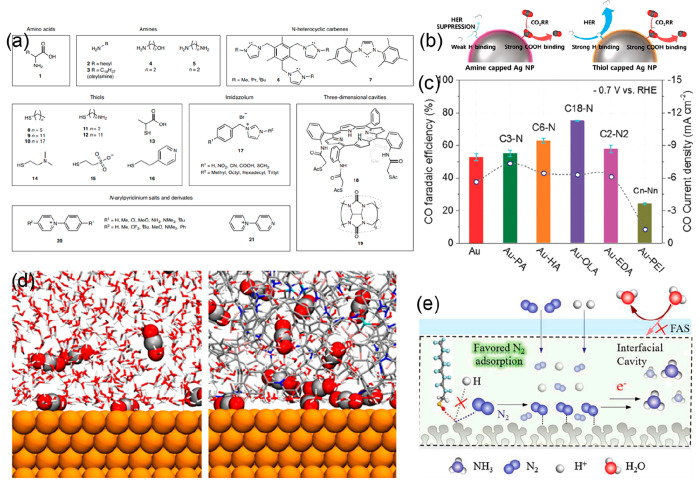
Figure 5.
(a) Surface modifiers grouped into different classes used to modulate the local chemical environment around the catalytic site (amino acids, amines, N-heterocyclic carbenes, thiols, imidazolium, three-dimensional cavities, N-arylpyridinium salts, and derivatives). Reproduced with permission from ref (26). Copyright 2020 Springer Nature. (b) Schematic of the product selectivity depending on the Ag NPs immobilized with an amine (or thiol)-containing anchoring agent. Reproduced with permission from ref (58). Copyright 2017 American Chemical Society. (c) FECO (column) and jCO (circle) of gold catalysts with different surface amine modifications in CO2-saturated 0.1 M KHCO3 at −0.7 V vs. RHE. Reproduced with permission from ref (59). Copyright 2018 Wiley. (d) Interface structure after 12 ns molecular dynamics simulations with a water–Cu interface and a random copolymer with a water–Cu interface. Color code: Cu, orange; C, gray; O, red; N, blue; F, pink; S, cyan; and H, white. Reproduced with permission from ref (68). Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. (e) Possible NRR mechanism at the surface of the hydrophobic catalyst. Reproduced with permission from ref (73). Copyright 2021 Elsevier.