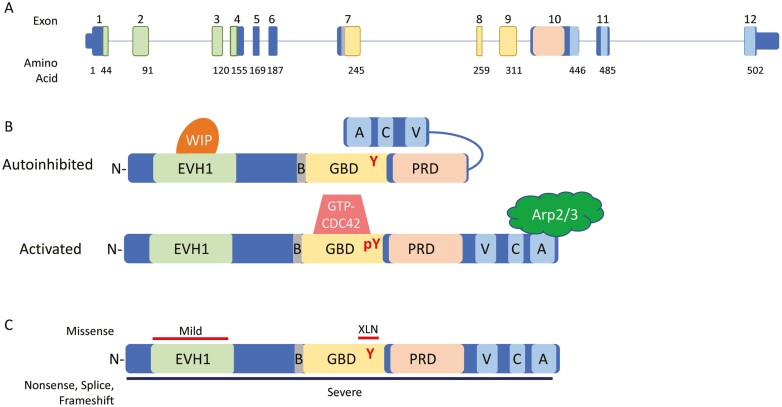
Figure 1:
WAS gene and WASP protein. (A) Genomic schematic for the WAS gene. Exons are numbered above; the number of the last amino acid coded in each exon is shown below. Exons encoding protein domains are colored accordingly. (B) Linear protein cartoon of WAS showing inhibited structure (top) with Y291 buried by folding of VCA domains and activated (bottom) with removal of WIP and binding of GTP-CDC42 allowing interaction with Arp2/3 complex. (C) Location of mutations leading to differing phenotypes. Missense mutations shown on top with red bars corresponding to phenotype, nonsense, splice, and frameshift mutations occur throughout, denoted by black bar below. Abbreviations: N, N-terminus: EVH1, ENA/Vasp homology 1 domain; B, basic domain: GBD, GTPase binding domain; PRD, proline rich domain; V, verprolin homology region; C, cofilin homology region; A, acidic sequence; WIP, WASP interacting protein.