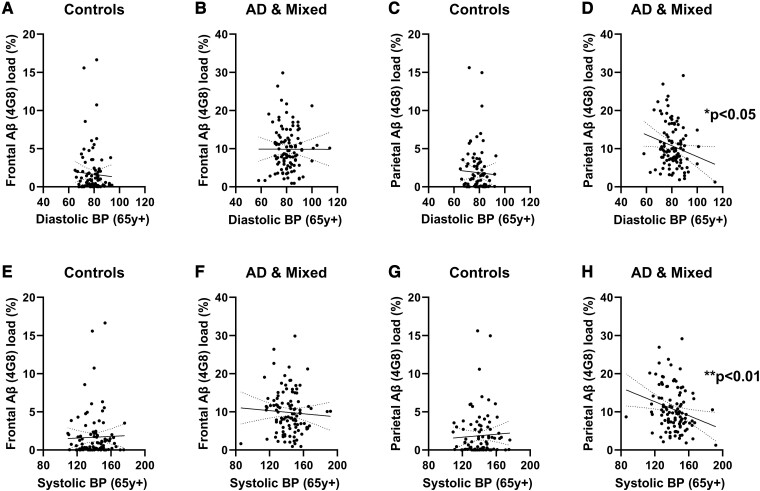
Figure 1.
Elevated DBP and SBP in late life were associated with reduced parenchymal Aβ load in the PC in Alzheimer's disease and mixed dementia. No relationship was seen between DBP and frontal Aβ load in (A) controls (Spearman’s correlation, n = 97, r = −0.0043, ns) or in (B) Alzheimer’s disease and mixed cases (n = 106, Spearman’s r = −0.0398, ns). No relationship was seen between DBP and parietal Aβ load in (C) controls (n = 92, r = −0.02337, ns). However, late-life DBP was associated with lower parietal Aβ (4G8) load in (D) Alzheimer’s disease and mixed dementia cases (n = 104, r = −0.2050, P = 0.0368). Late-life SBP did not correlate with frontal Aβ load in either (E) controls (n = 97, r = 0.05707, ns) or (F) Alzheimer’s and mixed dementia cases (n = 106, r = −0.1189, ns). Late-life SBP also did not correlate with parietal Aβ load in (G) controls (n = 92, r = 0.0907, ns). However, in Alzheimer’s disease and mixed dementia cases, late-life SBP correlated with lower (H) parietal Aβ load (n = 104, r = − 0.2570, P = 0.0084). Each point represents a single case. The continuous and interrupted lines indicate the best-fit linear regression and 95% CIs. Abbreviations: Ad = Alzheimer’s disease; BP = blood pressure; FC = frontal cortex; PC = parietal cortex; y = years.