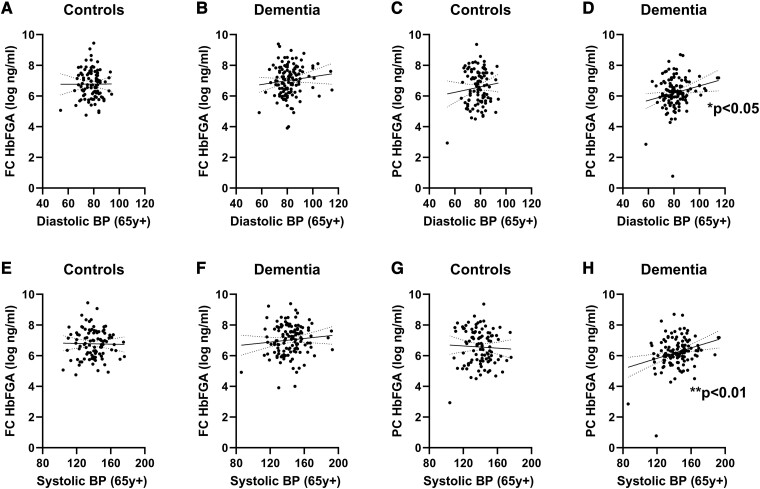
Figure 4.
Elevated DBP and SBP in late life were associated with higher parietal cortical Hb-adjusted FGA levels in dementia. No relationship was seen between DBP and FC HbFGA in (A) controls (Pearson’s correlation, ns, n = 99) or in (B) dementia cases (ns, n = 126). Similarly, no significant relationship was found between DBP and PC HbFGA in (C) controls (ns, n = 99). Late-life DBP was associated with lower (D) PC HbFGA (Pearson’s r = 0.2119, P = 0.0186, n = 123). There was no relationship between late-life SBP and FC HbFGA in either (E) controls (ns) or (F) dementia cases (ns). There was no relationship between late-life SBP and PC HbFGA in (G) controls (ns). However, late-life SBP correlated positively with PC HbFGA in (H) dementia cases (Pearson’s r = 0.2719, P = 0.0023). Each point represents a single case. The continuous and interrupted lines indicate the best-fit linear regression and 95% CIs. Abbreviations: BP = blood pressure; FC = frontal cortex; HbFGA = haemoglobin-adjusted fibrinogen; PC = parietal cortex; y = years.