Figure 1. Acute BP effects of graded levels of CPAP in awake patients with autonomic failure and supine hypertension (Protocol 1).
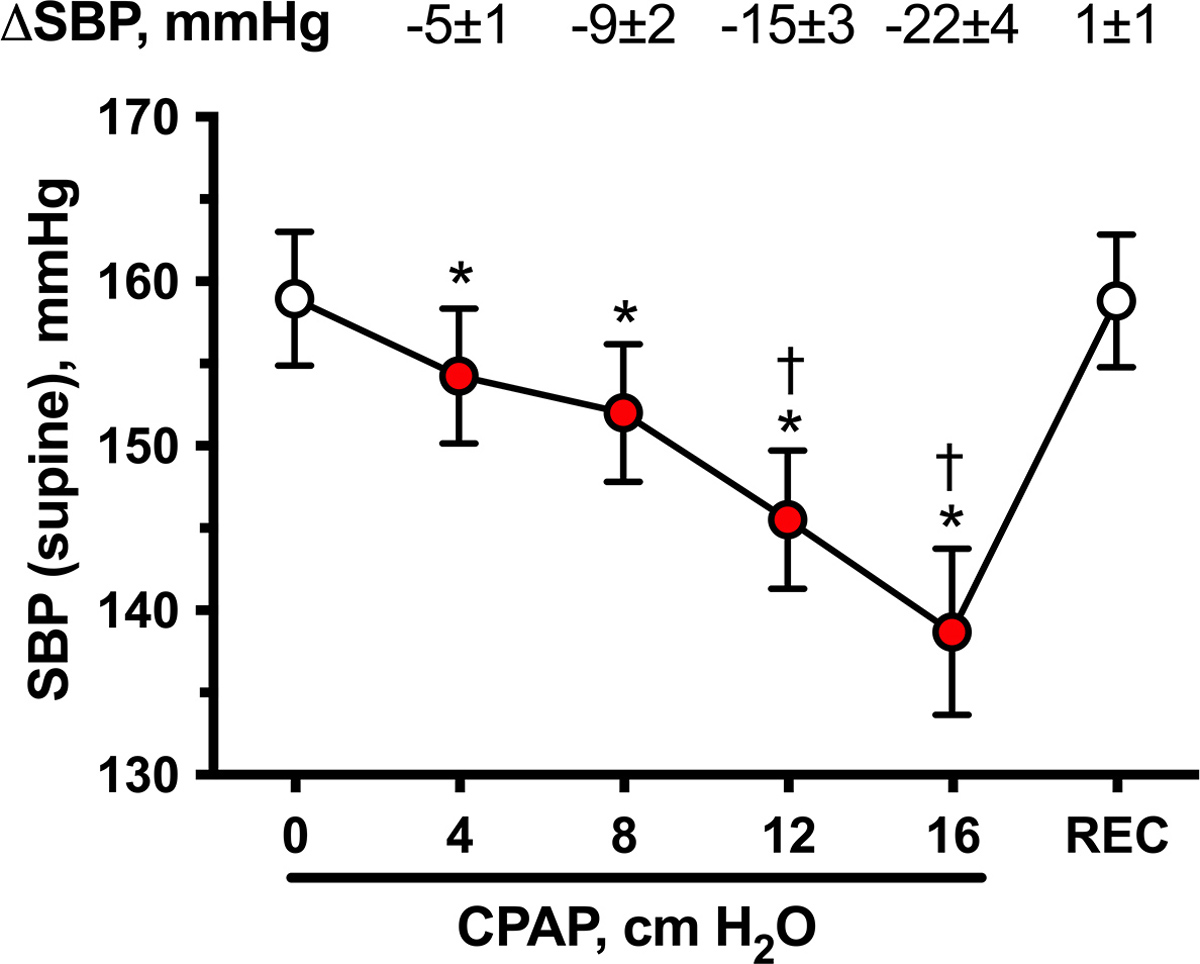
Supine systolic BP (SBP) and their changes from baseline (CPAP 0; ΔSBP) during increasing levels of CPAP (4, 8, 12, and 16 cm H2O for 3 minutes each) and immediately after recovery (REC). CPAP produced an acute dose-dependent decrease in SBP. Values are expressed as mean±SEM. Overall differences were analyzed by a mixed-effects model (P<0.001). *P<0.05 versus baseline (CPAP 0) and †P<0.05 versus the preceding CPAP level, adjusted for multiple comparisons using Bonferroni correction.
