Figure 2. Acute hemodynamic effects of graded levels of CPAP in awake patients with autonomic failure and supine hypertension (Protocol 1).
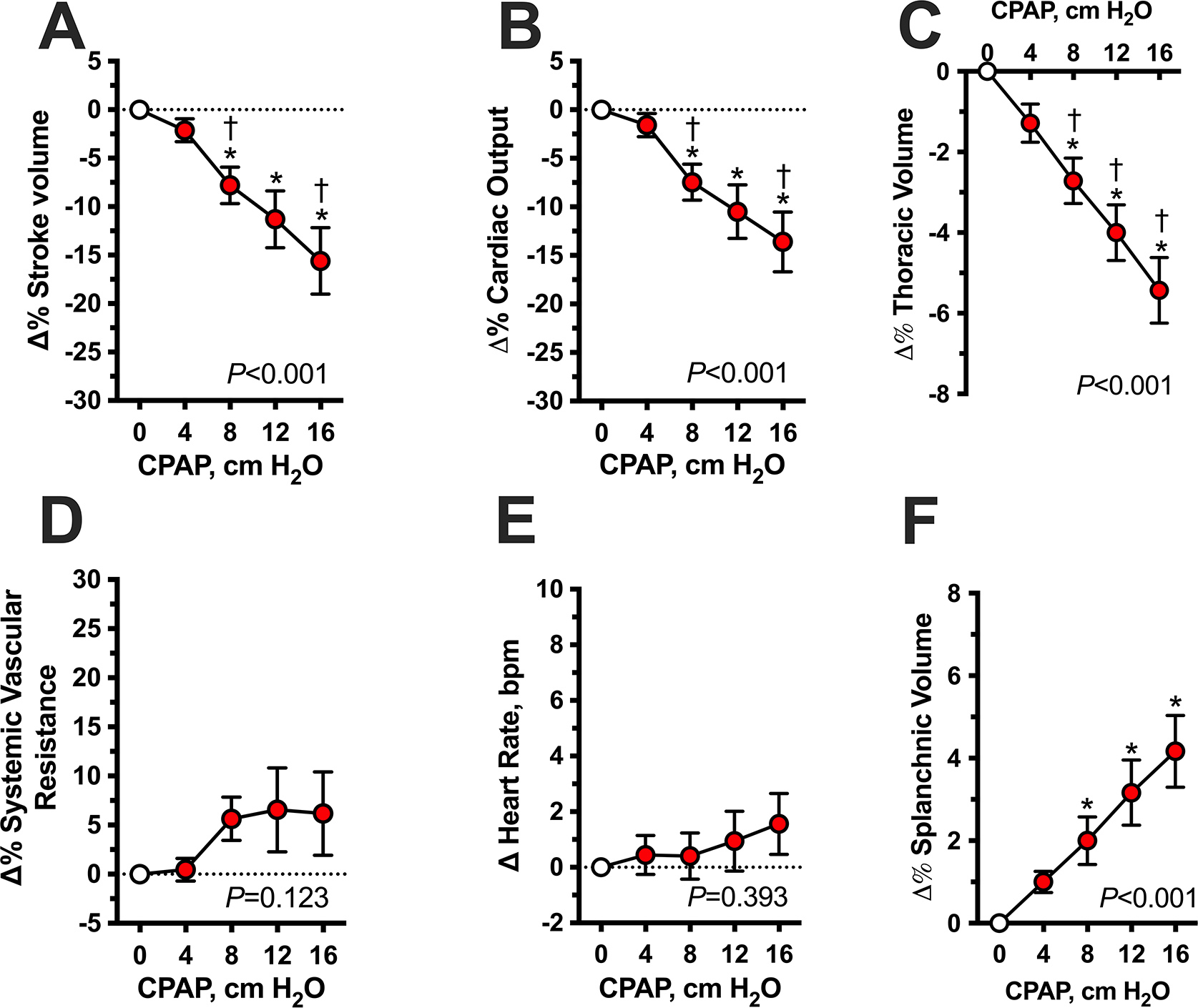
Hemodynamic parameters are expressed as percent changes (Δ%) from baseline (CPAP 0) during increasing levels of CPAP (4, 8, 12 and 16 cm H2O for 3 minutes each). CPAP produced an acute dose-dependent decrease in stroke volume (A), cardiac output (B) and thoracic volume (C) with a concomitant increase in abdominal volume (F). Systemic vascular resistance (D) and heart rate (E) did not change significantly. Values are expressed as mean±SEM. P values for overall differences were analyzed by mixed-effects model. *P<0.05 versus baseline (CPAP 0) and †P<0.05 versus the preceding CPAP level, adjusted for multiple comparisons using Bonferroni.
