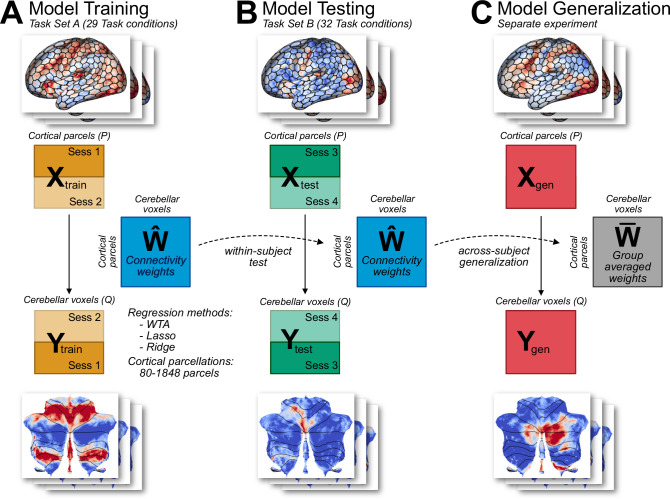
Figure 1. Connectivity model training and evaluation.
(A) Models were trained on Task Set A (session 1 and 2) of the multi-domain task battery (MDTB; King et al., 2019). Model hyperparameters were tuned using fourfold cross validation. Three types of models were used (WTA, Lasso, Ridge), each with 7 cortical parcellations of different granularity. (B) Models were tested on an independent Task Set B (sessions 3 and 4), which included both novel and common tasks. Models had to predict the cerebellar activity solely from cortical activity patterns. To avoid the influence of shared noise correlations across cortex and cerebellum, the models were trained and tested by using cortical and cerebellar activity patterns from different sessions within each task set (see Methods). (C) As a test of generalization, the models were used to predict cerebellar activity from cortical data obtained from a separate experiment (King et al., unpublished data).