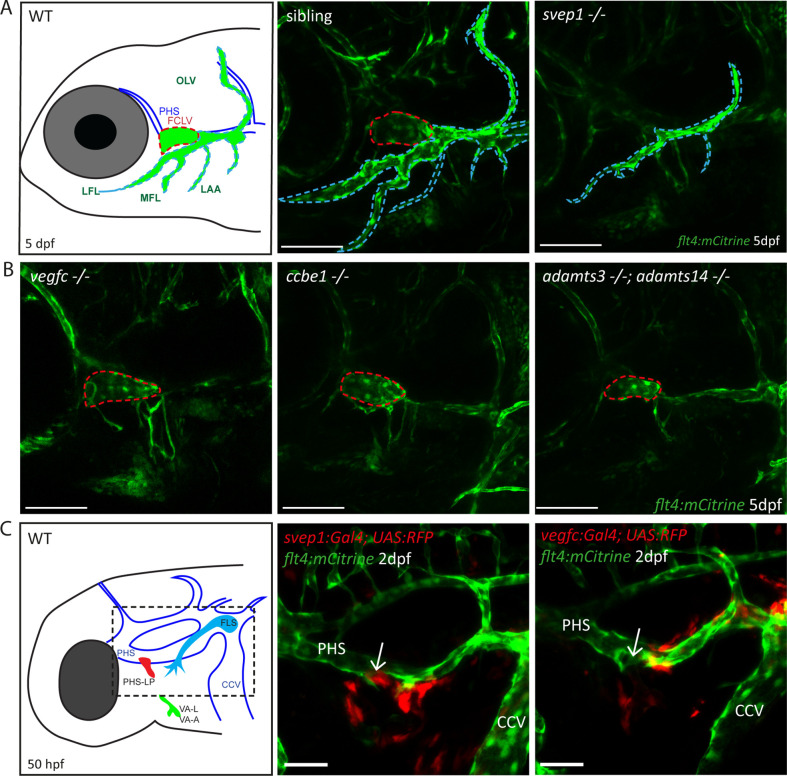
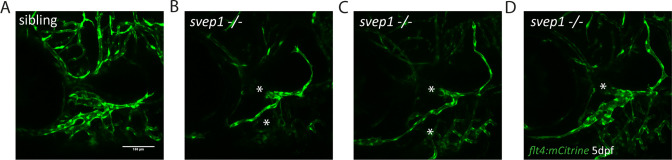
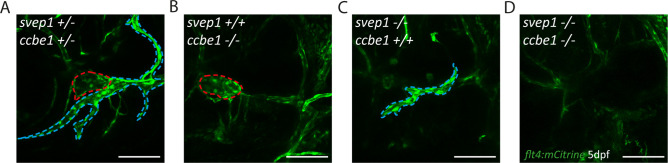
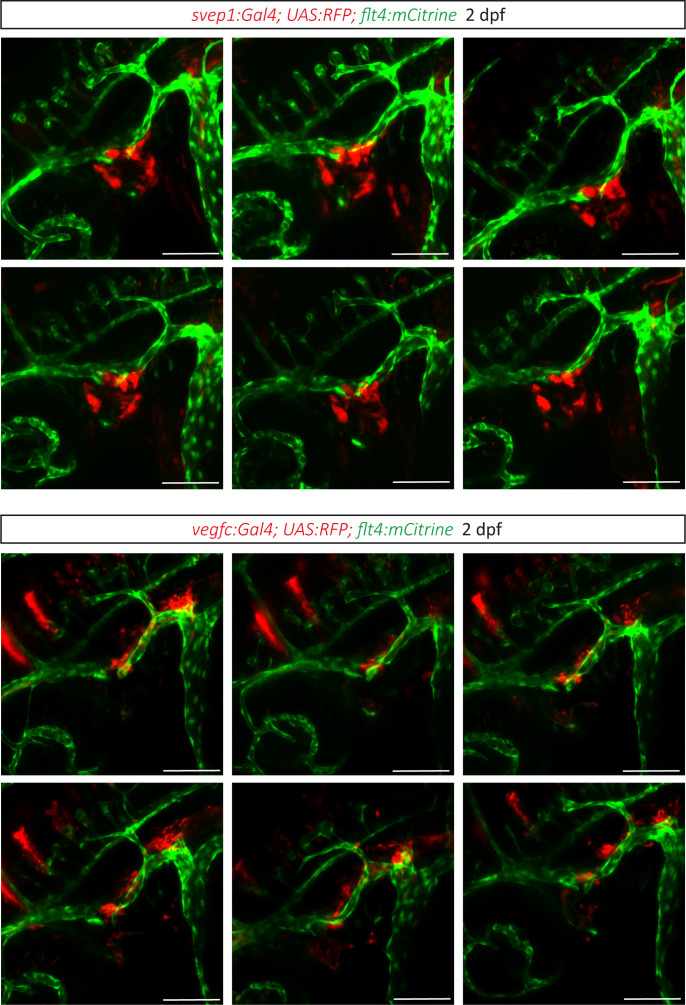
Figure 1. Svep1 is required for the development of the FCLV, in a Vegfc-independent manner.
(A) Schematic representation of facial lymphatic network at 5 dpf and maximum intensity projection of confocal images of flt4:mCitrine positive svep1 mutants (n = 10) and siblings (n = 6), highlighting facial lymphatic structures at 5 dpf. Scale bar = 100 µm. Note the absence of the FCLV (red dotted line) in svep1 mutants whereas other facial lymphatic structures are less strongly affected (OLV, LFL, MFL, and LAA marked by blue dotted lines). (B) Confocal images of flt4:mCitrine positive facial lymphatics in vegfc (n = 19), ccbe1 (n = 5), and adamts3;adamts14 (n = 2) mutants at 5 dpf. Scale bar = 100 µm. (C) Confocal images of svep1 and vegfc expression domains during sprouting from the PHS at 2 dpf, with schematic representation of different lymphatic progenitor populations. svep1 is expressed in close proximity to sprouting PHS-LPs, while vegfc expressing cells are more concentrated on the LECs arising from the CCV. Arrows point to sprouting PHS-LP. Scale bar = 50 µm. Expression patterns were confirmed in six embryos each (Figure 1—figure supplement 3). CCV, common cardinal vein; dpf, days post-fertilization; FCLV, facial collecting lymphatic vessel; FLS, facial lymphatic sprout; hpf, hours post-fertilization; LAA, lymphatic branchial arches; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; LFL, lateral facial lymphatic; MFL, medial facial lymphatic; OLV, otolithic lymphatic vessel; PHS, primary head sinus; PHS-LP, primary head sinus lymphatic progenitor; VA, ventral aorta; VA-A, ventral aorta angioblast; VA-L, ventral aorta lymphangioblast; WT, wildtype.