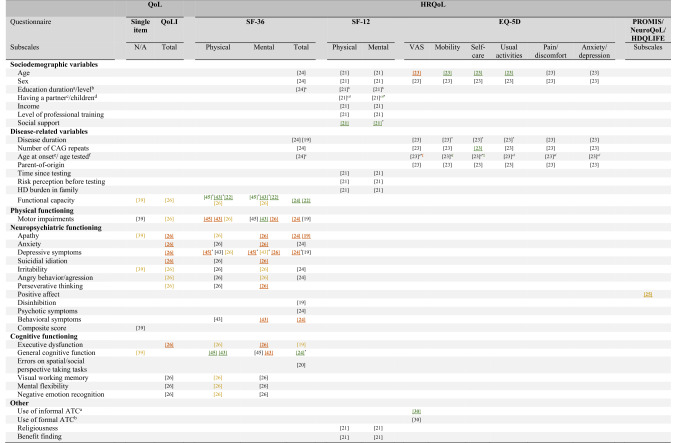
Table 2.
Bivariate findings of factors associated with (HR)QoL in HD
The numbers in the table correspond to the reference numbers in the reference list. For all (HR)QoL measures, a higher score indicates better (HR)QoL, except for the EQ-5D dimensions which display the severity of problems in a domain. For the associated variables, higher scores indicate more of that domain being measured (e.g., more motor impairments, more apathy, better functional capacity, and better cognitive functioning). References displayed in black indicate a non-significant relationship. Bold and underlined references indicate a significant association, with green referring to a positive relationship, whereas red to a negative relationship. Yellow indicates mixed findings, which are described in more detail in the manuscript
QoL quality of life, HRQoL health-related quality of life, SF-36 Medical Outcomes Study 36-Item Short Form Health Survey, SF-12 Medical Outcomes Study 12-Item Short Form Health Survey, EQ-5D EuroQol 5D, PROMIS Patient-Reported Outcomes Measurement Information System, HDQLIFE Huntington disease quality of life, QoLI Quality of Life Inventory, N/A not applicable, CAG cytosine–adenine–guanine, HD Huntington’s disease, ATC Assistive Technology for Cognition
*Associated factor was uniquely associated with (HR)QoL in multivariable/multivariate analyses. Other uniquely associated variables that were not reported in previous bivariate analyses (and, therefore, not reported in this table) were economic pressure [34], number of CAG repeat, age [43], functional capacity [30, 31], apathy [44], physical symptoms, psychological symptoms, depression-dejection, tension-anxiety [41], level of unmet needs [31]
aInformal ATC involves the use of external aids on one's own (e.g., using a cellphone, calendar, and planners)
bFormal ATC involves devices and/or software that is designed specifically to support people with cognitive impairment