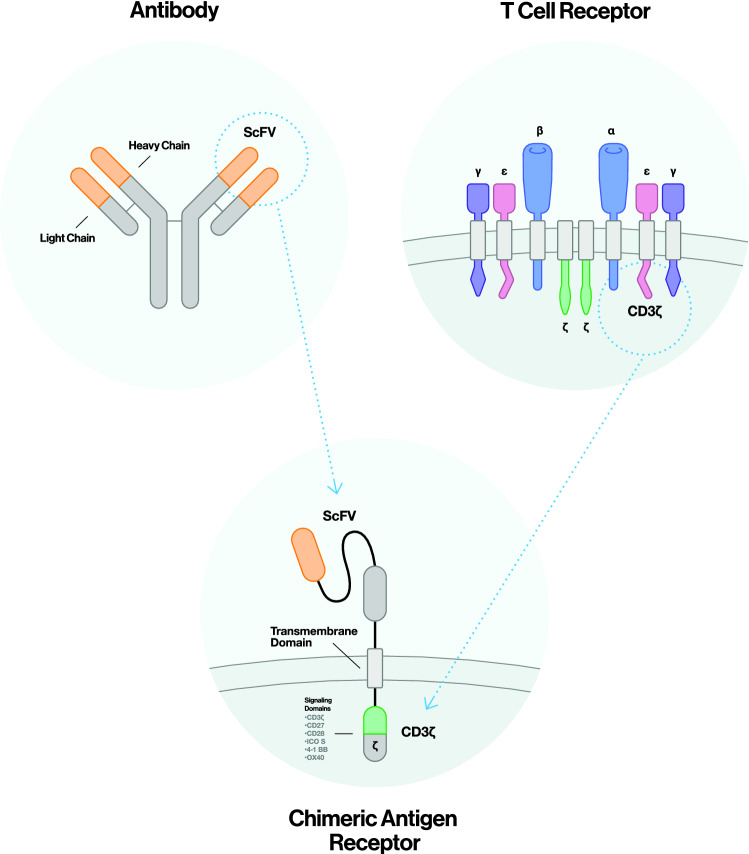
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of a CAR structure. A CAR is typically composed of a specificity-conferring scFv extracellular binding domain that is linked, via spacer/hinge and transmembrane domains, to a CD3ζ intracellular signaling moiety (less commonly an FcεRIγ domain) that can include one or more intracellular costimulatory domains (CD8, CD27, CD28, CD134, CD137, 41-BB, OX40). CARs can recognize target antigens in a non-MHC dependent manner. CAR chimeric antigen receptor, ScFV single-chain variable fragment