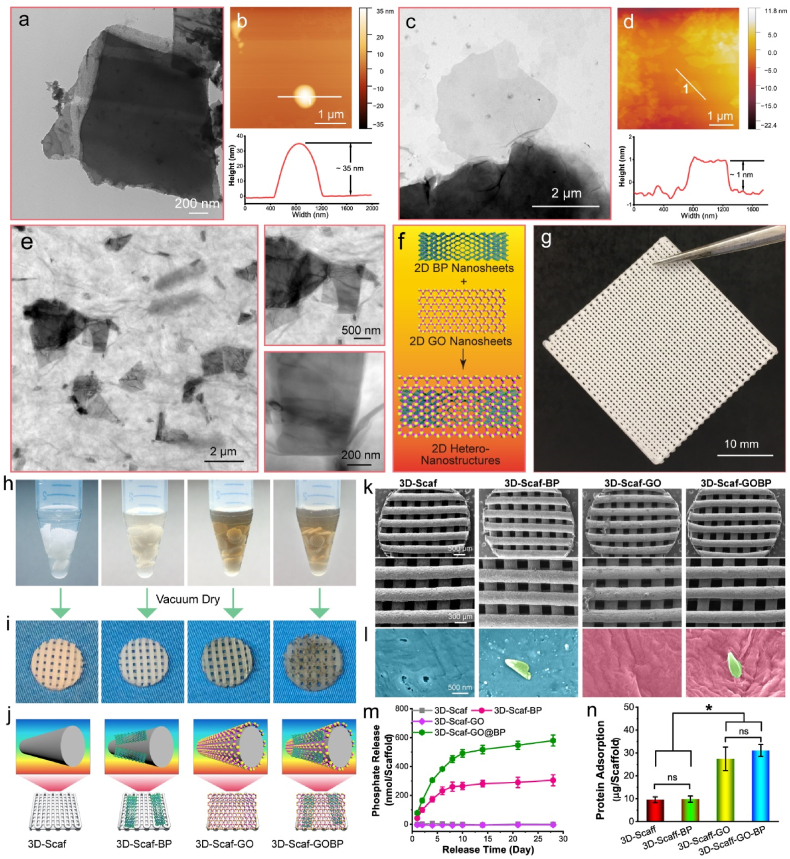
Fig. 2.
Scaffolds Characterization. a) TEM images and b) AFM characterization of BP nanosheets. c) TEM images and d) AFM characterization of GO nanosheets. e) TEM images and f) schematic demonstration of 2D hetero-nanostructures formed by GO nanosheets and BP nanosheets. g) Photograph of a 3D printed polymer sheet and h) the punched 3D scaffolds immersed in pure DI H2O solutions and solutions containing 2D BP nanosheets, GO nanosheets, or GOBP hetero-nanostructures for surficial functioning. i) Photographs and j) schematic demonstrations of the resulting 4 types of 3D scaffolds: plain scaffolds (3D-Scaf), scaffolds functionalized with 2D BP nanosheets (3D-Scaf-BP), GO nanosheets (3D-Scaf-GO), and GOBP hetero-nanostructures (3D-Scaf-GOBP). k) SEM images of the 3D scaffolds and scaffolds functionalized with 2D materials. l) Enlarged view of the surface morphology of the 4 types of 3D scaffolds with detailed indication of the polymer surface (cyan), BP nanosheets (green), and GO nanosheets (pink). m) Cumulative phosphate ion release profile and n) protein adsorption ability for the various functionalized 3D scaffolds. (*: p < 0.05; ns: not significant).