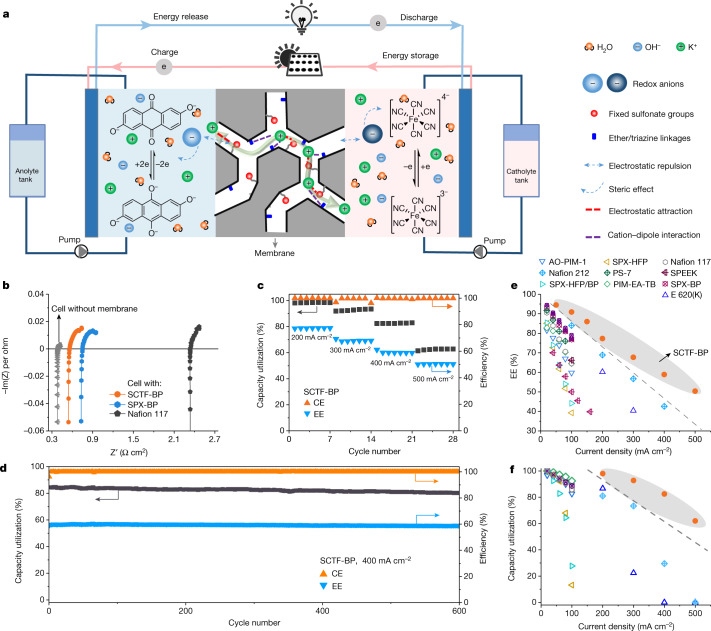
Fig. 4. SCTF-BP membrane enables rapid charging of aqueous alkaline quinone flow battery.
a, Schematic illustrating an alkaline quinone flow battery assembled with the SCTF-BP membrane, and conduction of K+ ions across the membrane matrix. The catholyte is ferrocyanide and the anolyte molecule is DHAQ. b, EIS spectra measured in cells assembled with SCTF-BP, SPX-BP and Nafion 117 membrane, respectively. The grey line represents the EIS spectrum of the cell without a membrane. c, Coulombic efficiency (CE), capacity utilization and EE of the cell assembled with SCTF-BP at varying current density. For each current density, seven repetitions were performed to ensure accuracy. Fluctuations were observed only when current density was switched. d, Galvanostatic cycling at a current density of 400 mA cm−2 for cells assembled with a SCTF-BP membrane. b–d, Electrolyte concentration 0.4 M. e,f, Energy efficiency (e) and capacity utilization (f) of quinone flow batteries assembled with commercial, PIM and SCTF-BP membranes are plotted as functions of current density. Symbols shown in inset in e apply also to f. e,f, Dashed lines and shading are a visual guide only; detailed values provided in Supplementary Table 5.