Figure 3.
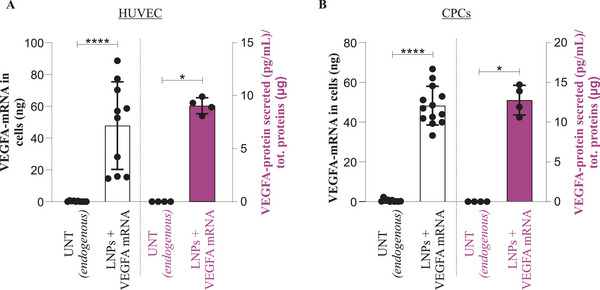
Delivery of translatable VEGF‐A mRNA to human umbilical vein endothelial cells and cardiac progenitor cells via lipid nanoparticles (LNPs). A 3 µg of VEGF‐A mRNA was delivered to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs) via LNPs. The levels of VEGF‐A mRNA and protein were quantified 24 h post LNP administration. A) Detection of LNP‐VEGF‐A mRNA in HUVECs (left side, Y‐axis) and its translation into VEGF‐A protein (right side, Y‐axis). The Mann‐Whitney U‐test was applied to compare the LNP treated and untreated samples. VEGF‐A mRNA (n = 10, for untreated, and treated), ***p < 0.001. VEGF‐A protein (n = 4, for untreated, and treated), *p < 0.05. B) Detection of LNP‐VEGF‐A mRNA in CPCs (left side, Y‐axis), and its translation into VEGF‐A protein (right side, Y‐axis). The Mann‐Whitney U‐test was applied to compare the LNP‐treated and untreated samples. VEGF‐A mRNA (n = 10 for untreated, n = 13 for treated), ****p < 0.0001. VEGF‐A protein (n = 4, for untreated, and treated), *p < 0.05.
