Figure 3.
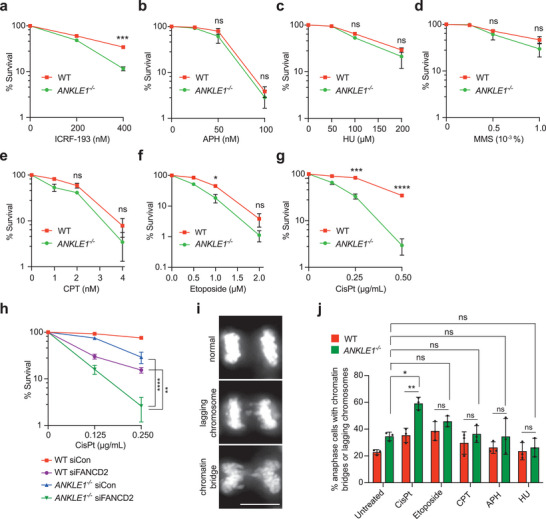
ANKLE1−/− cells are hypersensitive to cytotoxic drugs that induce chromatin bridges. a–g) Clonogenic cell survival assays were carried out on HCT116 wild‐type and ANKLE1−/− cells upon treatment of the indicated concentrations of cytotoxic drugs (ICRF‐193, APH: aphidicolin, HU: hydroxyurea, MMS: methyl methanesulfonate, CPT: camptothecin, etoposide and CisPt: cisplatin). Graphs show mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance values were determined with unpaired two‐tailed t‐tests. h) Clonogenic survival assay was carried out on cells treated with control siRNA or siRNA against FANCD2, followed by the treatment with indicated concentrations of cisplatin. Graphs show mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance values were determined with two‐way ANOVA. i) Representative images of anaphase cells harboring lagging chromosome and chromatin bridge. Scale bar, 10 µm. j) Cells were untreated or treated with CisPt (0.5 µg mL−1), CPT (10 × 10−9 m), APH (200 × 10−9 m) or HU (0.5 × 10−3 m) for 8 h followed by release into fresh medium for 16 h. Percentages of anaphase cells with lagging chromosome or chromatin bridges were quantified. Bars represent mean ± SD of n = 3 independent experiments. Statistical significance values were determined with unpaired two‐tailed t‐tests. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001; ns = not significant.
