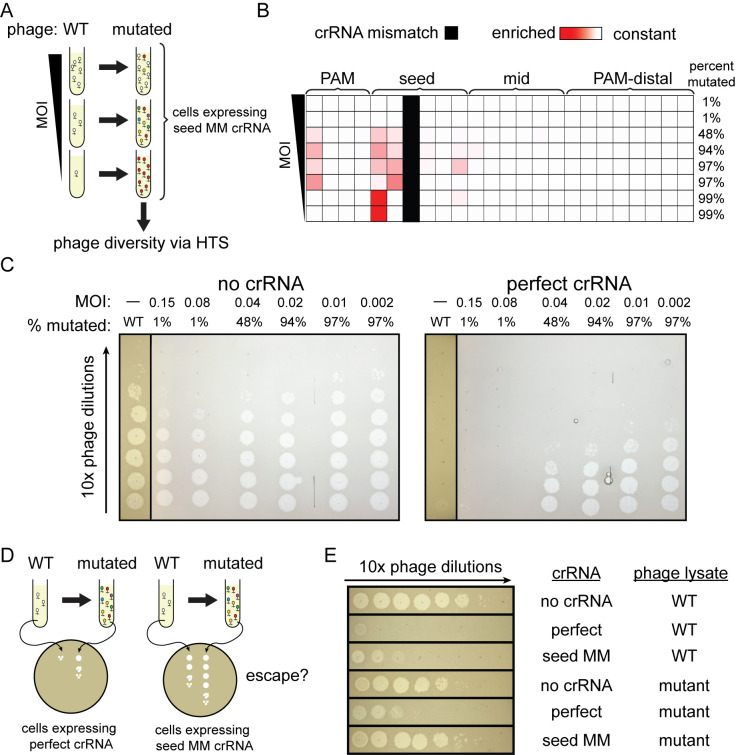
Fig 5. Combined mismatches are necessary for complete phage escape.
(A) Schematic for experiment to test the impact of MOI on escape phage diversity. Cultures expressing Cas12a and the position 3 mismatched crRNA targeting gene J were infected with lambda phage at varied MOIs. Mutant phages in lysates were detected by high-throughput sequencing. (B) Heat map showing the position of phage mutations that arose when infecting bacteria expressing seed mismatch crRNA at different MOIs. Phage was harvested from liquid cultures containing bacteria expressing FnCas12a and a crRNA with a C-T mismatch at position 3. Phage was added to the culture at mid-log phase at a range of MOIs starting at 0.15 and serial 2-fold dilutions from 1/2 to 1/32 and an additional sample at an MOI of 1.5 × 10−3. Phage was harvested 5 h after infection. High-throughput sequencing was used to determine the percent of phages in each that had a mutation in the target region. The heat map shows the positions in the target that were enriched with mutations. These positions are colored darker red according to their Z-score relative to the control phage population. Z-scores range from 0 (white) to 10.1 (darkest red). The position of the initial crRNA mismatch is indicated in solid black. See S8 Data for quantification of variant abundance. (C) Spot assays using phage isolated from liquid cultures as described in (A) on bacteria expressing a matching crRNA. Phage harvested in (A) was 10-fold serial diluted and spotted on bacteria with a crRNA matching the wild-type lambda phage genome target (matching crRNA) or bacteria without a crRNA guiding Cas12a (no crRNA). Wild-type phage controls were spotted on these same bacterial strains. Phages harvested from the lowest MOI cultures were omitted due to their low titer which prevented visible plaque formation on the CRISPR active E. coli strain. See S11B Fig for full plates. (D) Schematic for experiment shown in panel (E). Wild-type or mutant phage populations were used for spot assays on plates with lawns of E. coli expressing Cas12a and either the perfect or the seed mismatched crRNA to determine whether the combination of the preexisting mismatch and newly acquired target mutations are necessary for complete escape from Cas12a targeting. (E) Spot assays using mutationally diverse phage on bacteria expressing crRNAs with and without mismatches. Phage was isolated from the liquid culture as described in (A) that was initially infected with phage diluted 1:8. Mutated phage and unmutated control phage (WT) were then used for spot assays on bacterial lawns expressing FnCas12a and a matching crRNA (perfect), a crRNA with the original seed mismatch, or no crRNA as negative control.