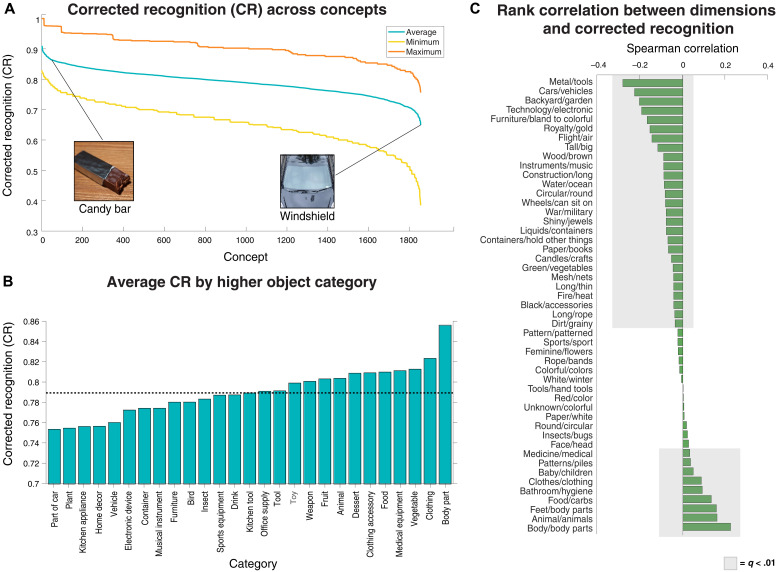
Fig. 1. Descriptive analyses of memorability across the concept and category levels of the THINGS database and the 49 object dimensions.
(A) The spread of CR across the 1854 object concepts revealed that not all concepts are equally memorable. For concepts like candy bars, the entire range of component image memorability values was contained above the average value for a concept like windshields. (B) Visualizing the same spread across higher-order categories revealed variation in average memorability across the 27 categories, with some categories including part of car displaying a CR score below the overall average memorability of 0.793 represented by the dotted horizontal line, while others like body parts displayed a score above the average. (C) This high variability in memorability continues when examining the correlation between memorability and embeddings along the object dimensions. Thirty-six of 49 dimensions displayed a significant association with memorability (shaded bars, FDR-corrected q < 0.01), with 9 showing a positive relationship (e.g., body/body parts being more memorable) and 27 showing a negative relationship (e.g., metal/tools being less memorable). Note that in this figure, THINGS database images were replaced by similar looking images from the public domain images available in THINGSplus (48).