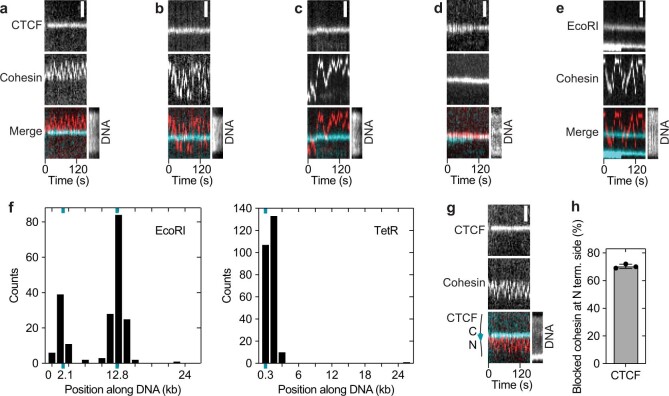
Extended Data Fig. 2. Cohesin diffusion assay characterization.
a–d, Examples of cohesin diffusion on DNAs with CTCF bound at its binding site. Cohesin was labelled with Alexa 660 (red). CTCF was labelled with tetramethylrhodamine (TMR) (cyan). Sytox Green DNA stain was introduced into the flow cell at the end of the experiment. Scale bar, 2 μm. (a) Example of cohesin diffusion blocked by CTCF. (b) Example of cohesin diffusing past CTCF multiple times within the imaging timeframe. (c) Example of cohesin diffusing past CTCF in one direction only. Example of cohesin diffusing past CTCF in one direction only. This behaviour was observed very infrequently (2 ± 3% of N = 264 events). This could be because cohesin-CTCF encounters were recorded after the system has reached equilibrium and so all the single-pass events had occurred before we could image them. It is unknown why some cohesin molecules were able to pass CTCF multiple times (Extended Data Fig. 2b). (d) Example of cohesin-CTCF colocalization. e, Example of cohesin diffusing past TMR-labelled EcoRIE111Q. f, Positions of DNA bound (left) Janelia Fluor 646-labelled EcoRIE111Q and (right) TMR-labelled TetR, which were flowed into flow cells at the end of diffusion experiments to determine the DNA orientation and hence the orientation of the CTCF binding site at position 10,452 bp. EcoRI restriction sites were present at positions 2,177 bp and 12,802 bp out of 26,123 bp. N = 201. Six TetO sequences were present at positions 40–274 bp. N = 251. g, As in main Fig. 1f, except using a DNA in which the CTCF site was inverted. h, Fraction of blocked events that diffused on the DNA between the tether point and the N terminal side of CTCF using the DNA template as used in (g) (mean ± SD (N = 48) from 3 independent experiments).