Figure 4. Mapping of the BBSome-binding determinant on TOM1L2.
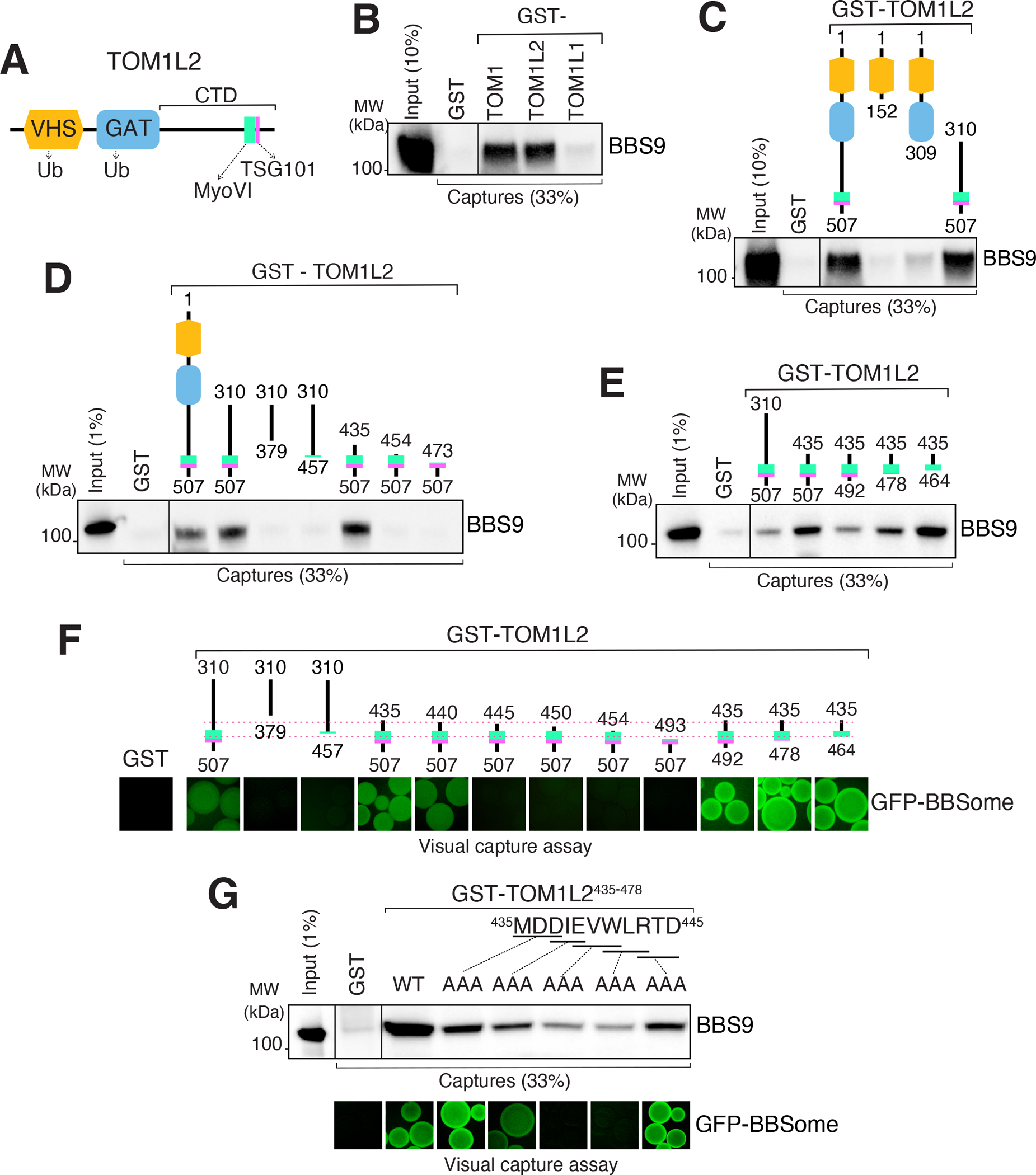
A. Diagram of the domain organization of TOM1L2. B. GST-TOM1, GST-TOM1L2 and GST- TOM1L1 were immobilized on glutathione sepharose and beads incubated with BBSome purified from the bovine retina. Bound material was eluted in SDS sample buffer and the BBSome was detected by immunoblotting for BBS9 (and BBS4 and BBS5, see Fig. S5A). The purity of the GST fusion proteins is shown in the Ponceau stains found in Fig. S5A. C. Capture assays of pure BBSome were conducted with truncations of TOM1L2 fused to GST. See Fig. S5B for additional immunoblots and Ponceau stain. D-E. Capture assays with truncations of TOM1L2 find that aa 435–464 are necessary and sufficient for binding to the BBSome. F. Visual capture assays were conducted with truncations of TOM1L2 fused to GST and immobilized onto glutathione sepharose and extracts from HEK293 cells overexpressing all eight BBSome subunits fused to GFP. G. TOM1L2 triple alanine mutants were fused to GST and immobilized onto glutathione sepharose and used for conventional capture assays with BBSome purified from bovine retinas (upper panel) or for visual capture assays with extracts from HEK293 cells overexpressing all eight BBSome subunits fused to GFP (lower panel).
