Fig. 3.
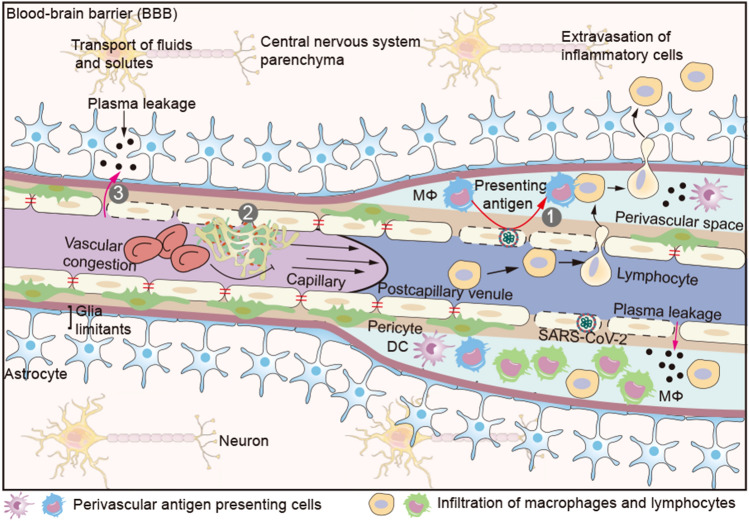
Blood–brain barrier (BBB). The BBB consists primarily of capillary and postcapillary venule, pericyte, basement and astrocyte end-feet. The endothelial basement and astrocyte end-feet form an enclosed space (perivascular space) at the postcapillary venules, in which a few antigen presenting cells (APCs) reside. Extravasation of immune cells into the brain parenchyma occurs at the level of postcapillary venules. Activated immune cells can only cross the endothelial barrier, but not the astrocyte end-feet. Only after a second recognition of their cognate antigen on perivascular APCs, these activated lymphocytes can enter brain parenchyma. (1) Perivascular APCs (macrophage or DC) infiltrate (SARS-CoV-2) infected ECs and present cognate antigens to activated lymphocytes for entry into the brain parenchyma. (2) Damaged cerebrovascular ECs promote (micro) thrombi and aggravate brain hypoxia. (3) Increased vascular pressure due to microthrombi pushes plasma into the brain parenchyma at the site of endothelial barrier injury. Serum proteins such as fibrin (ogen), thrombin, and plasmin (ogen) can activate microglia enhancing neurons death. DC dendritic cell; Mφ macrophage