Fig. 6. Acute alcohol exposure increases inflammation and altered adipokines in RptorAKO mice.
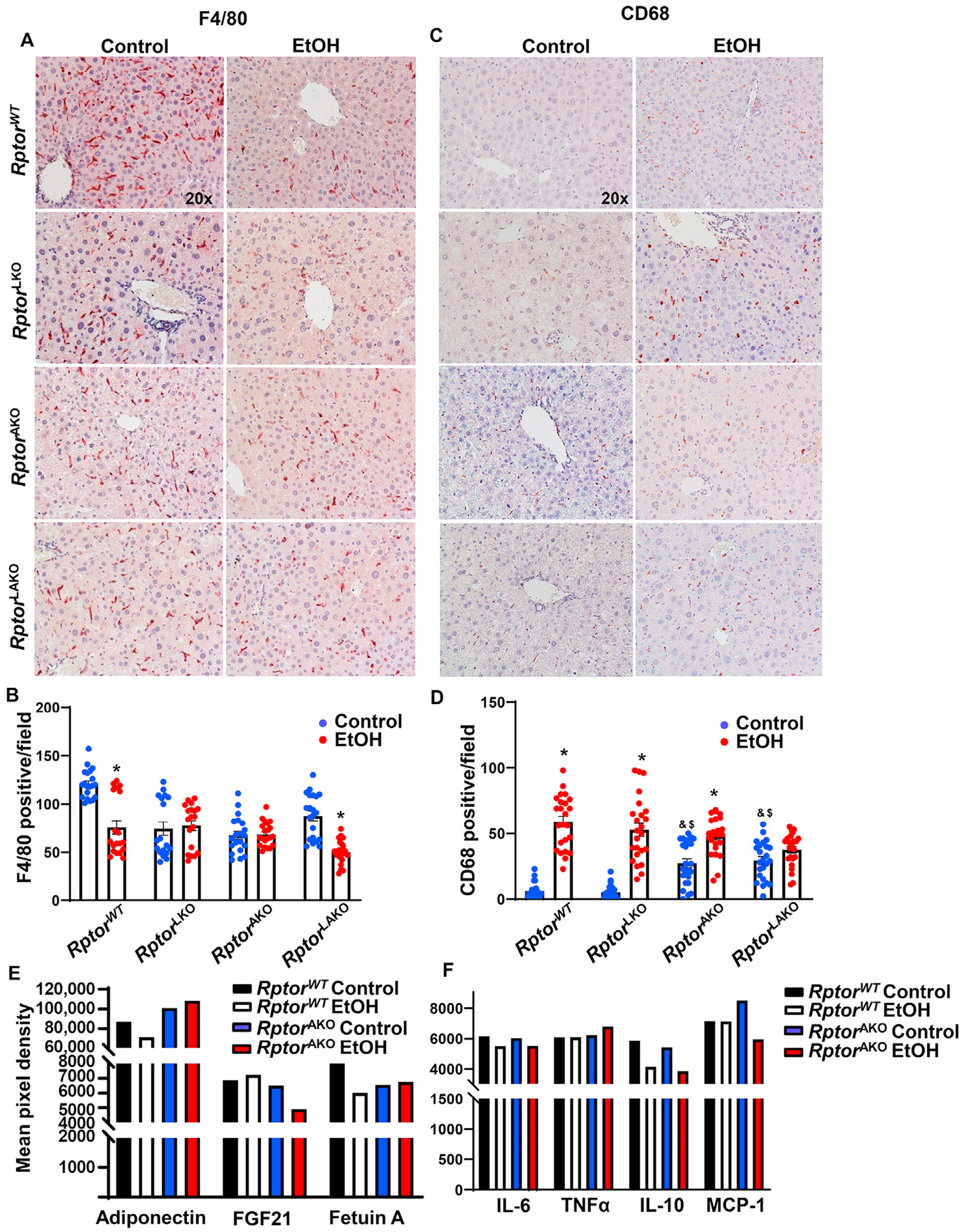
Mice were treated as in Fig. 4. (A) F4/80 was stained in the livers by immunohistochemistry staining and (B) F4/80 positive macrophages were quantified. (C) CD68 was stained in the livers by immunohistochemistry staining and (D) CD68 positive macrophages were quantified. (E, F) Equal amount of serum from the same group was pooled. Circulating adipokines (E) and inflammatory mediators (F) were analyzed by Proteome Profiler Mouse Adipokine Array Kit. Data are expressed as means ± SEM and subjected to one-way ANOVA with Turkey post hoc test. n = 3 (A–D); n = 4–7 (E–F). *P < 0.05 EtOH vs. control; #P < 0.05 vs. WT EtOH; ^P < 0.05 vs. LKO EtOH; &P < 0.05 vs. WT control; $P < 0.05 vs. LKO control. Original magnification, × 20. Abbreviations: EtOH, ethanol; FGF21, fibroblast growth factor 21; IL-6, interleukin-6; IL-10, interleukin-10; KO, knockout; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1; Rptor, regulatory-associated protein of mTOR; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TG, triglyceride; WT, wild-type.
