Figure 1: Subsets of thymic epithelial cells described in human thymus and their representative markers.
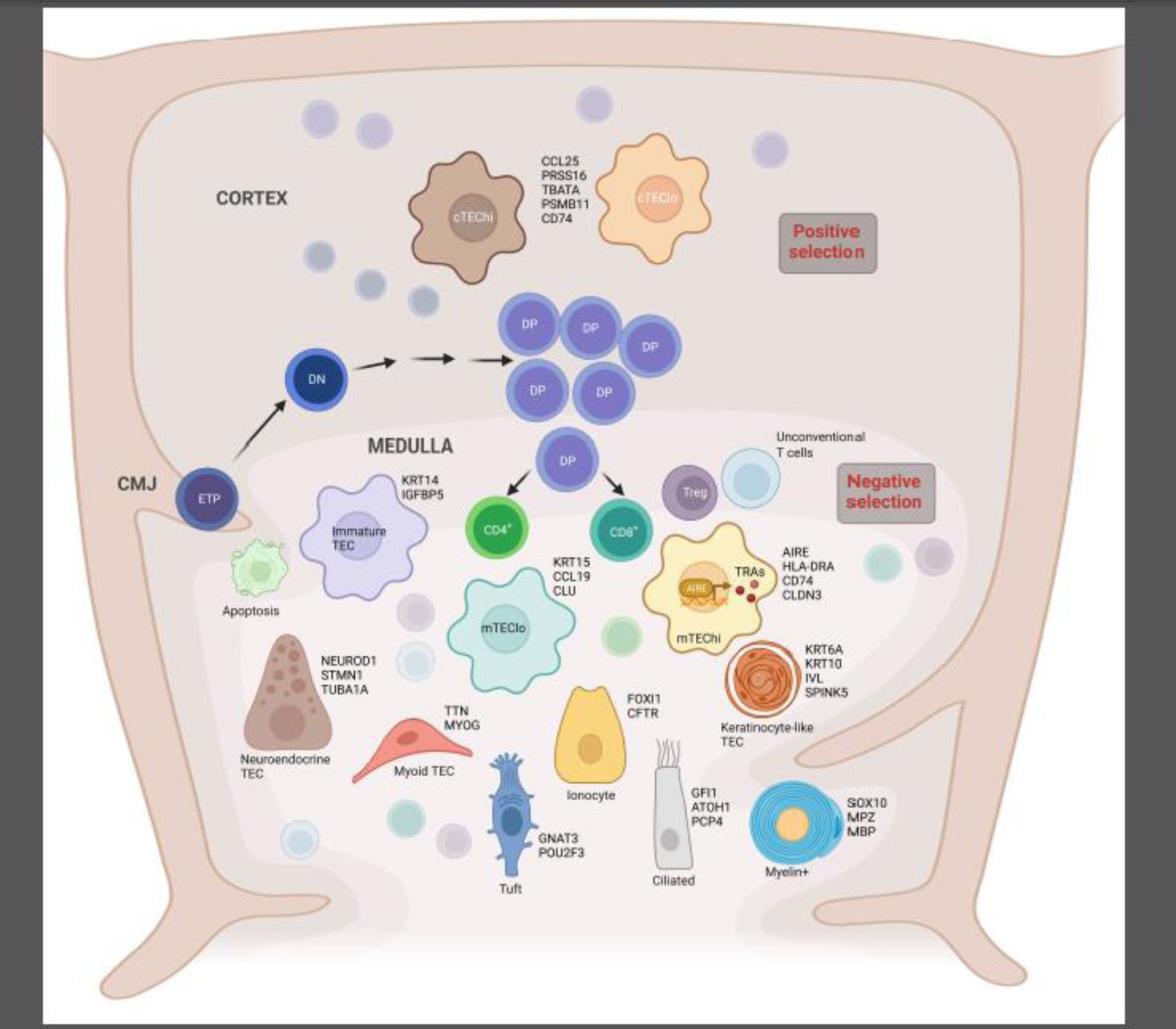
Simplified schematic representation of T cell development in human thymus, indicating the early stages of development from the entrance of bone marrow-derived early thymic progenitors (ETP) at the cortico-medullary junction (CMJ), through the different steps of their positive selection in the cortex, from CD4− CD8− double negative (DN) to CD4+ CD8+ double positive (DP). The thymocytes then move to the medulla where they complete their maturation, undergo negative selection to eliminate self-reactive T cell specificities and give rise to the different subsets of mature T cells: CD4+, CD8+, T regulatory cells (Treg) and unconventional T cells. Cortical thymic epithelial cell (cTEC) and medullary TEC (mTEC) subsets recently described in human thymus are represented here. For each epithelial cell subset, some of the specific markers are listed.
