FIG 5.
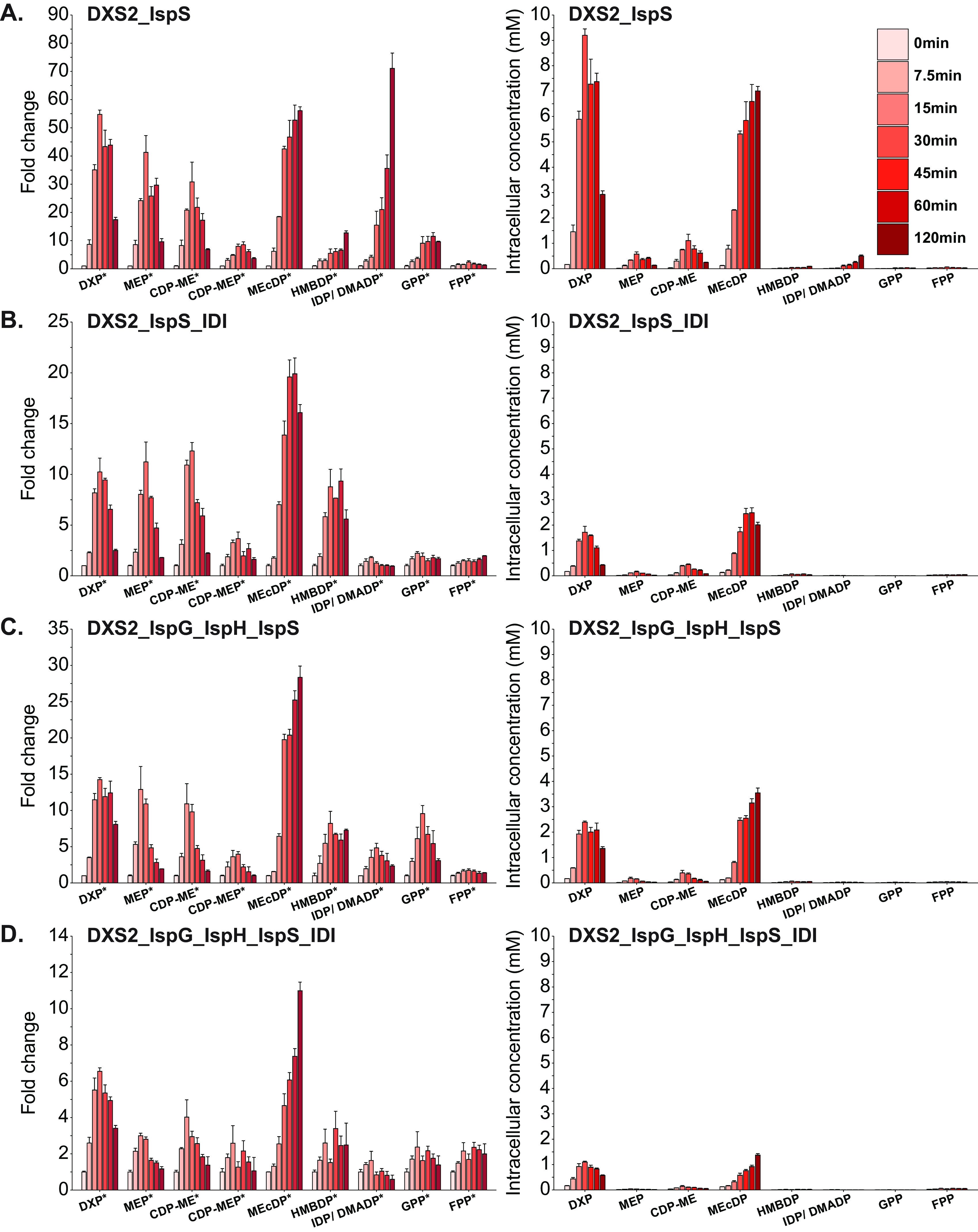
The overexpression of isoprene synthase in combination with other MEP pathway enzymes decreases carbon accumulation in the MEP pathway resulting from individual DXS2 overexpression. Fold change data (left) relative to preinduction (time point 0) metabolite levels and absolute metabolite concentrations (right) for MEP metabolites at 7.5, 15, 30, 45, 60, and 120 min postoverexpression of DXS2 and IspS (A); DXS2, IspS, and IDI (B); DXS2, IspG, IspH, and IspS (C); and DXS2, IspG, IspH, IDI, and IspS (D). Data represent averages of three biological replicates. Error bars show ± standard deviation. Some error bars are too small to be visible in this representation. Asterisks located next to metabolite names on the X-axis indicate statistical significance of at least one datapoint within the time course for the indicated metabolite (FDR, <0.05). DXP, 1-deoxy-d-xylulose 5-phosphate; MEP, 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 4-phosphate; CDP-ME, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-d-erythritol; CDP-MEP, 4-diphosphocytidyl-2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 2-phosphate; MEcDP, 2-C-methyl-d-erythritol 2,4-cyclodiphosphate; HMBDP, 4-hydroxy-3-methylbut-2-enyl diphosphate; IDP, isopentenyl diphosphate; DMADP, dimethylallyl diphosphate; GPP, geranyl pyrophosphate; FPP, farnesyl pyrophosphate; DXS2, DXP synthase; IspG, HMBDP synthase; IspH, HMBDP reductase; IDI, IDP isomerase; IspS, isoprene synthase.
