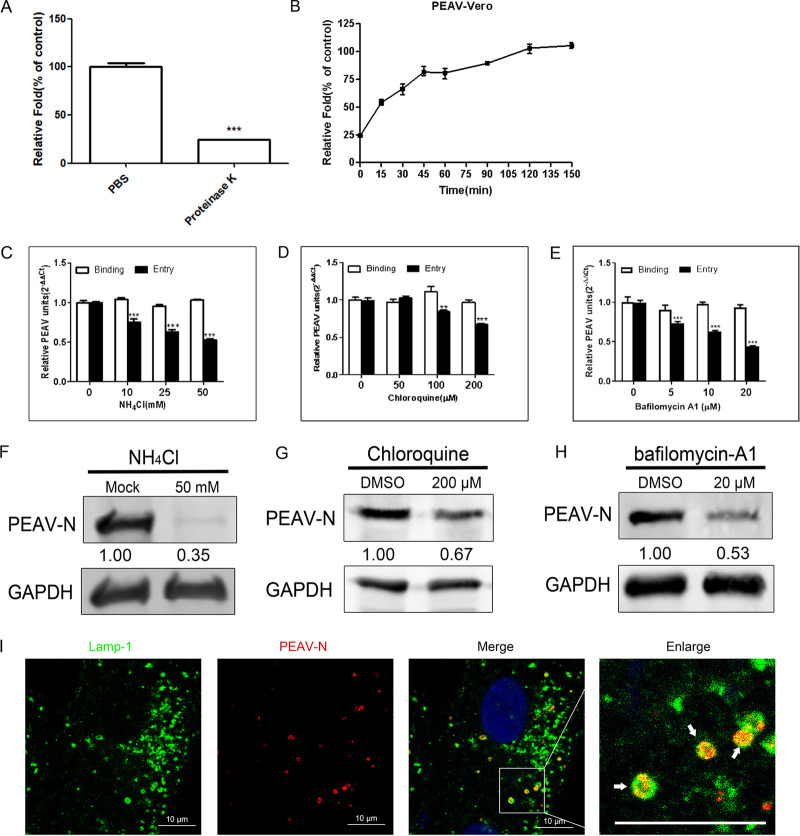
FIG 1.
PEAV entry depends on pH. (A) Vero cells were inoculated with PEAV (MOI = 1) (1 h, 4°C), treated with proteinase K (5 min, 20°C), washed, and lysed. Extracted viral RNA levels were detected using qRT-PCR. PBS was used as a control. (B) Vero cells were inoculated with PEAV (MOI = 1) (1 h, 4°C), washed, and incubated with preheated maintenance medium (37°C, 0 to 150 min). Cells were treated with proteinase K for different durations, and RNA levels were detected using qRT-PCR. (C to E) Vero cells were pretreated (37°C, 15 min) with different concentrations of endosomal acidification inhibitors (NH4Cl, chloroquine, and bafilomycin-A1), followed by incubation with PEAV (MOI = 1) to allow binding (1 h, 4°C) and entry (37°C, 1 h) in the presence of drugs. All results are presented as the mean ± SD from three independent experiments (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001). (F to H) Vero cells were inoculated with PEAV (MOI = 5) in the presence of the NH4Cl (50 mM), chloroquine (200 μM), and bafilomycin-A1 (20 μM) for a prolonged infection period (2.5 h, 37°C). Western blotting was performed to detect the early expression of PEAV N protein. Relative protein content was calculated using ImageJ software. (I) Vero cells were inoculated with PEAV (MOI = 10) (1 h, 4°C), washed, incubated (30 min, 37°C), and fixed (4% PFA, 15 min, room temperature). Virus particles and lysosomes were stained with anti-PEAV N and anti-Lamp-1 monoclonal antibodies, respectively, and their respective localizations were observed using a confocal microscope. The white arrow shows that PEAV colocalizes with lysosomal vesicles. Scale bar = 10 μm.