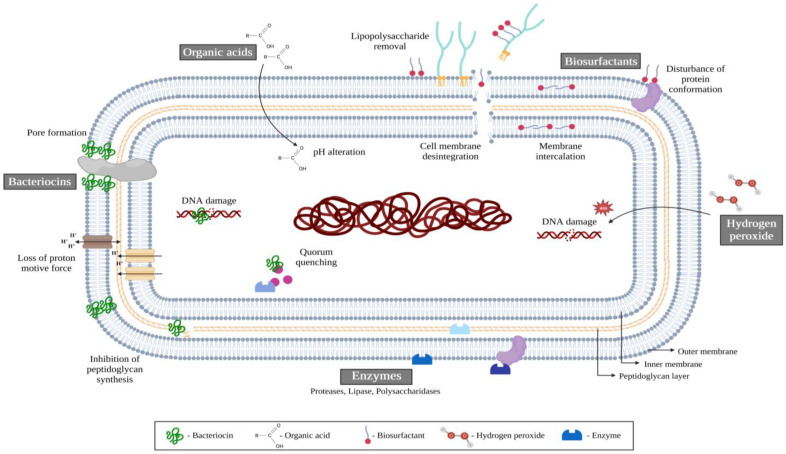
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of action of probiotics against foodborne microorganisms. Bacteriocins can induce cell death by dissipating the proton motive force and disrupting bacterial membranes. Organic acids lead to a decrease in pH, impairing the growth of microorganisms. Biosurfactants affect cell surface compounds, causing membrane disintegration. Hydrogen peroxide can damage biomolecules such as DNA. Enzymes can target and damage extracellular proteins, exopolysaccharides, DNA, or QS molecules. Adapted from [30,43].