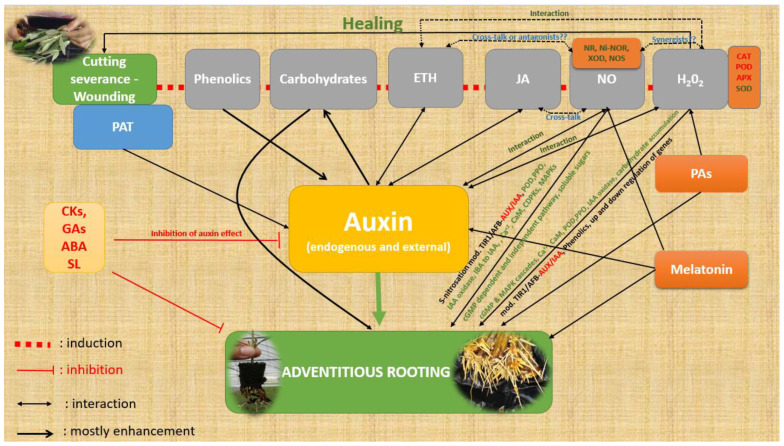
Figure 5.
A simplified presentation of the factors described in this manuscript that influence ARF. Red letters indicate the catabolic activity of enzymes or reduction or inhibition, green letters indicate induction, activation, or increase, and black letters indicate modifications in general (increase/decrease). Interaction indicates the relationship between the specific compounds concerning ARF. ETH, ethylene; JA, jasmonates; NO, nitric oxide; NR, nitrate reductase; Ni-NOR, nitrite–NO reductase; XOD, xanthine oxidase; NOS, NO synthase-like enzymes; PAs, polyamines; CKs, cytokinins; Gas, gibberellins; ABA, abscisic acid; SL, strigolactones; PAT, polar auxin transport; POD, peroxidase; PPO, polyphenoloxidase; CAT, catalase; APX, ascorbate peroxidase; SOD, superoxide dismutase; IAA, indole-3-acetic acid; IBA, indole-3-butyric acid; CaM, calmodulin; cGMP, cyclic guanosine monophosphate; CDPKs, Ca2+-dependent protein kinases; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TIR1/AFB (TRANSPORT INHIBITOR RESPONSE 1/AUXIN SIGNALING F-BOX).