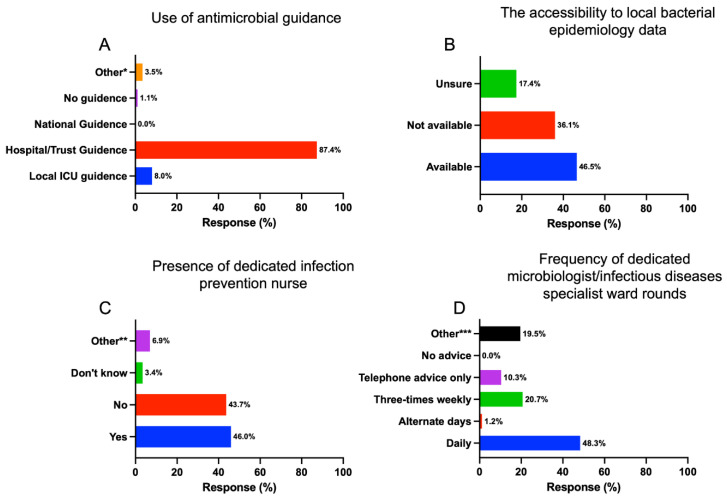
Figure 1.
The responses for the use of antimicrobial guidance (A), the accessibility to local bacterial epidemiology data (B), the presence of a dedicated infection prevention nurse (C), and the frequency of specialist ward rounds (D). * 3.5% highlighted using all forms of guidance along with microbiology-led recommendations. ** Nearly 7% of comments highlighted the use of link nurses between ICU and infection control nurses available to the wider hospital rather than specifically dedicated to ICU; *** Circa 20% included once weekly 5 days a week and weekends by phone, telephone ward rounds mostly weekdays, a mixture of virtual and MDT ward rounds. Comments noted the use of Microsoft Teams as a platform used to complete multidisciplinary ward rounds. There were no responses highlighting no access to microbiology or infectious diseases services.