Figure 6.
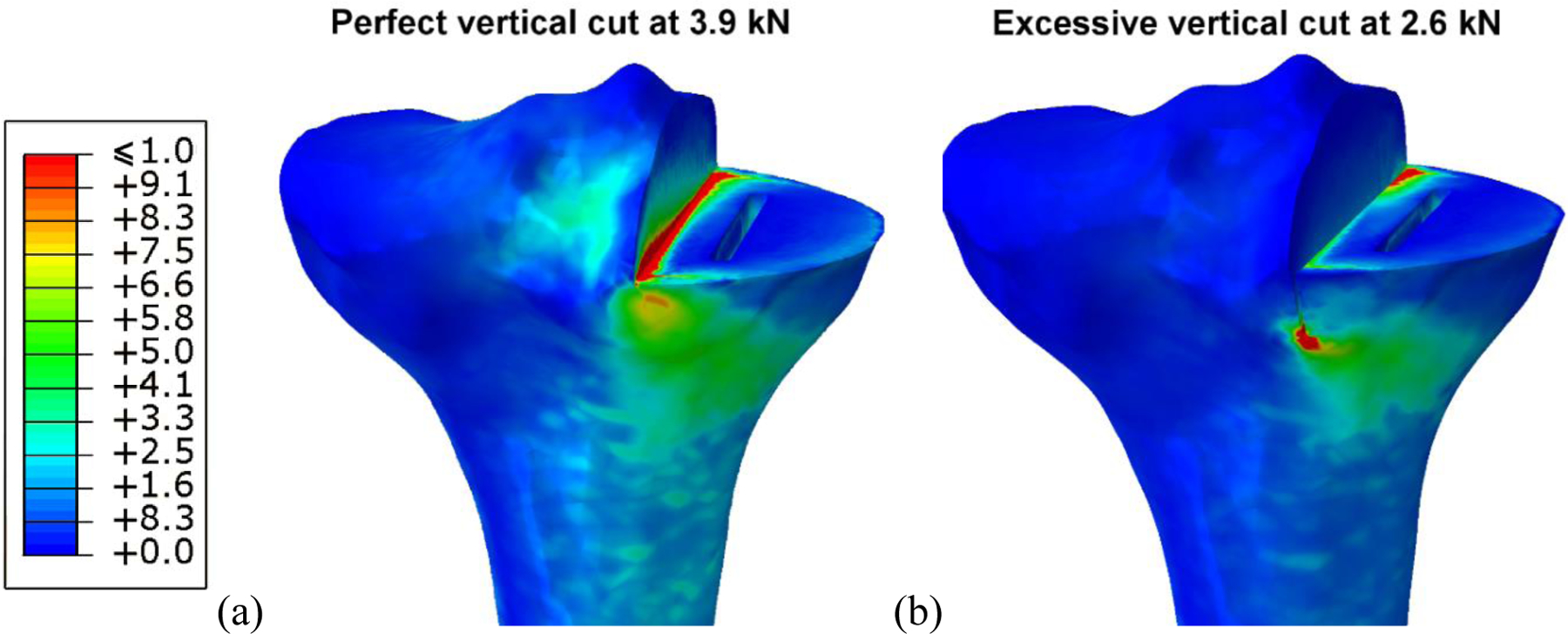
Distribution of the risk of fracture through a perfectly cut tibia loaded at 3.9 kN (a), and a tibia with excessive vertical cut loaded at 2.6 kN (b). Both models represent conditions which caused tibial fracture in experiments performed by Clarius et al.. The region most at risk of fracture extends diagonally from the vertical cut to the tibial cortex, via the keel.
