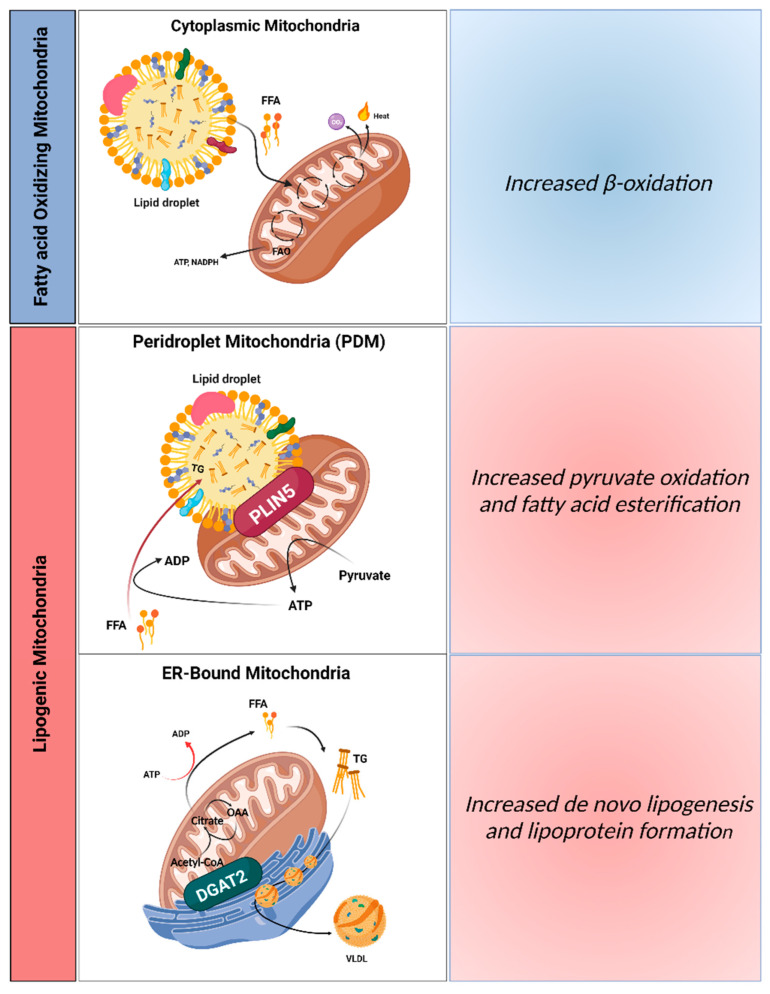
Figure 1.
Distinct mitochondrial populations in hepatocytes. Mitochondria attached to different organelles can have distinct roles, reinforcing the hypothesis that not all mitochondria in the same cell are homogeneous. This concept supports the assumption that some mitochondria in hepatocytes can be specialized in synthesizing lipids, while other mitochondria can oxidize lipids. The functional segregation of mitochondria can be determined by their anchorage to specific organelles, which prevents motility and thus fusion between the different subpopulations. In this context, it is believed that three mitochondrial populations exist in hepatocytes: (1) cytosolic mitochondria, which are responsible for fatty acid oxidation, production of ketone bodies, and ureagenesis to support glucose production; (2) mitochondria attached to lipid droplets, namely peridroplet mitochondria (PDM), which promote the esterification of fatty acids into triglycerides; and (3) ER-anchored mitochondria, responsible for fatty acid synthesis, lipoprotein assembly, and excretion. VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein; PLIN5, perilipin 5; DGAT2, diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 2; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; OAA, oxaloacetate. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 5 February 2023).