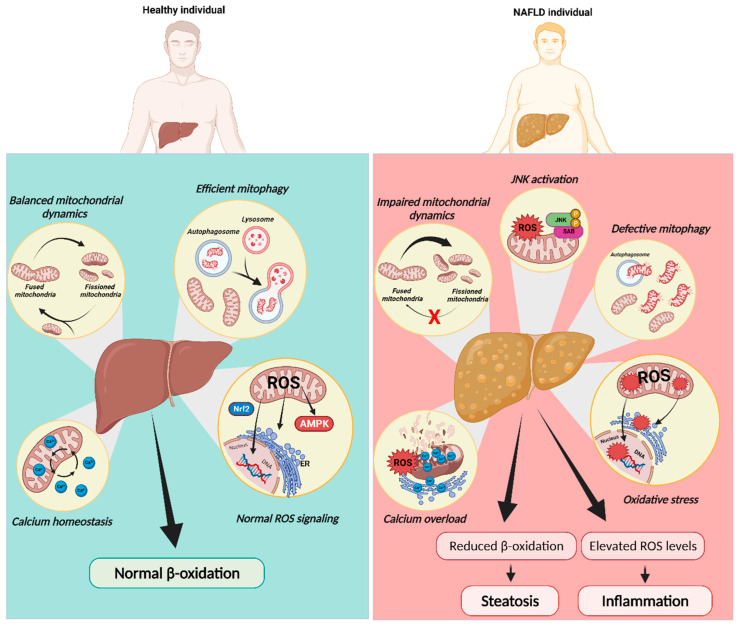
Figure 3.
Mitochondrial dysfunction in NAFLD progression. Mitochondria rely on diverse mechanisms to preserve their function including dynamics, redox signaling, mitophagy, and calcium homeostasis. In contrast to a healthy liver, mitochondria in NAFLD were reported to be fragmented and overloaded with calcium, with decreased oxidative capacity and increased ROS production, which cause JNK activation. JNK activation itself can induce these same defects in mitochondrial function, constituting a feed-forward cycle of mitochondrial dysfunction. Mitochondrial dysfunction in NAFLD was also explained by defective mitophagy. The decrease in fatty acid oxidation (FAO) caused by this compromise in mitochondrial function may induce FA accumulation in hepatocytes while impairing insulin signaling. ER, endoplasmic reticulum; JNK, c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase; SAB, SH3 homology associated BTK-binding protein; ROS, reactive oxygen species. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 5 February 2023).