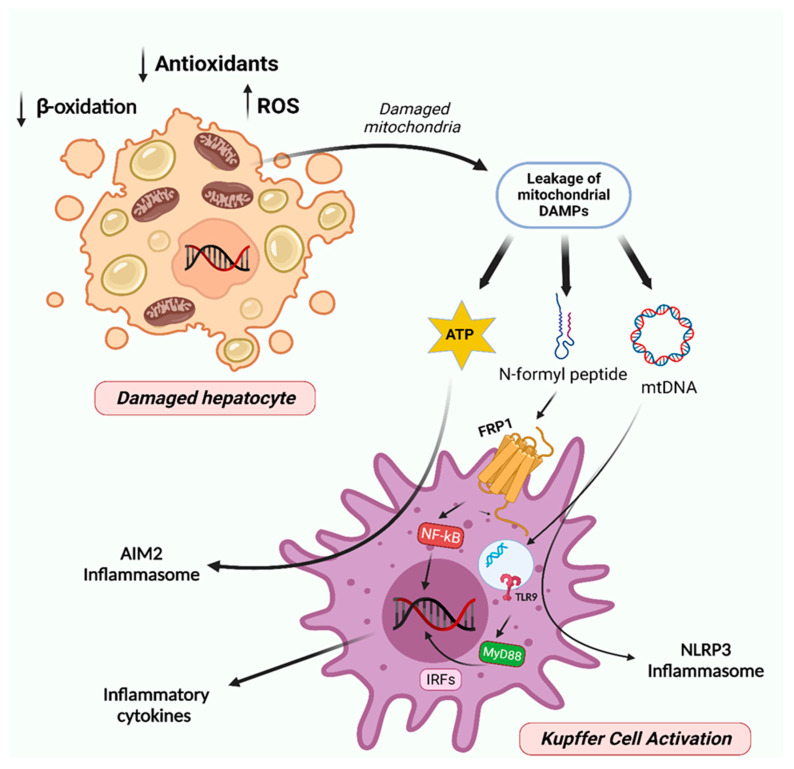
Figure 4.
Mitochondria involvement in NAFL progression to steatohepatitis and fibrosis. The augmented accumulation of damaged/dysfunctional mitochondria within hepatocytes results in cell necrosis and induces the leakage of mitochondrial DAMPs, such as mtDNA, N-formyl peptides, and ATP. Further, these signals trigger the activation of toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9) and formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1), which in turn activates the IRFs and NF-kB and thereby the production of inflammatory cytokines. mtDNA and ATP also activate the inflammasomes NLRP3 and AIM2, respectively. Multiple inflammatory cytokines and the activation of inflammasomes provide a chronic inflammatory milieu, which contributes to the development of steatohepatitis and fibrosis. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 5 February 2023).