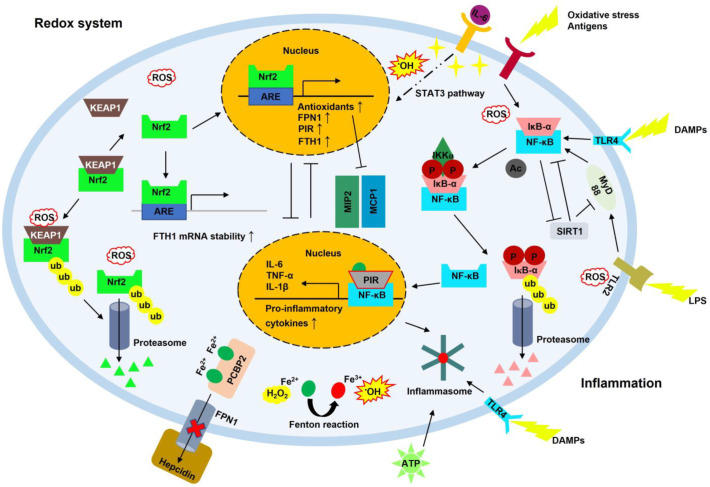
Figure 3.
The regulation of cellular redox balance and inflammation. In redox regulation, ROS produced by IL-6 or the Fenton reaction promotes the dissociation of Nrf2 from Keap1 and activates Nrf2. Activated Nrf2 is translocated to the nucleus and initiates the transcription of antioxidant enzymes and proteins requiring iron. This process protects cells from ROS. During inflammation, ROS, DAMPs, or LPS activate NF-κB signal transduction by eliminating IκB-α via ubiquitination. NF-κB moves to the nucleus and induces the transcription of pro-inflammatory cytokines. In this process, inflammasomes are activated, and inflammation is increased. To prevent excessive inflammation, the Nrf2 pathway is activated, which suppresses inflammation-related proteins, such as inflammasomes, MIP2, MCP1, and the NF-κB pathway. Additionally, SIRT1 acts as a regulator and inhibits the activation of NF-κB. NF-κB also regulates the activation of the uncontrolled redox system by inhibiting Nrf2 activation. ARE, antioxidant response element; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; FPN1, ferroportin 1; FTH1, ferritin heavy chain; •OH, hydroxyl radical; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; IκB-α, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha; IKKα, IκB kinase alpha; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; KEAP1, Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MCP1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; MIP2, macrophage inflammatory protein 2; MyD88, myeloid differentiation primary response protein 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; Nrf2, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; P, phosphorylation; PCBP2, poly(rC)-binding protein 2; PIR, pirin; ROS, reactive oxygen species; SIRT1, silent information regulator factor 2-related enzyme 1; STAT3, signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TLR2, Toll-like receptor 2; TLR4, Toll-like receptor 4; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-alpha; Ub, ubiquitin.