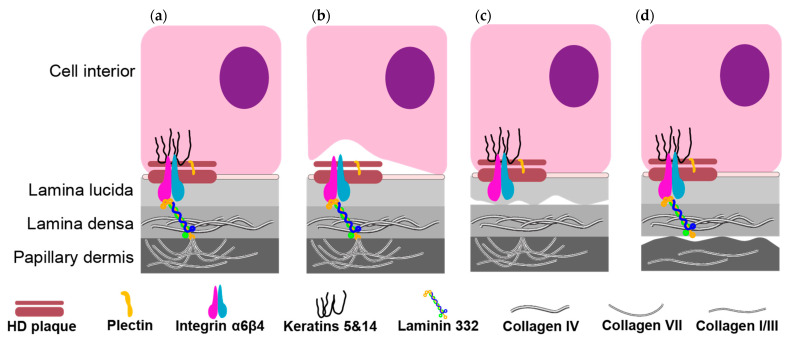
Figure 1.
Graphic representation of the skin dermo-epidermal junction and targeted molecules associated with different types of EB. (a) The dermo-epidermal junction of healthy skin. The epidermal keratinocytes are strongly attached to their underlying extracellular matrix through structures called the hemidesmosomes (HD). The transmembrane receptors integrins α6β4, intermediate the connection of the extracellular laminin 332 with the keratin intermediate filaments cytoskeleton in the cell interior; (b) Cleavage in EBS occurs within the basal layer keratinocytes due to mutations within the genes encoding keratins, components of the intermediate filaments. The lack of the intermediate filaments cytoskeleton results in a disruption of epidermal keratinocytes strong adhesion to its underlying basement membrane at the level of the HD; (c) Disruption of keratinocyte cell adhesion at the level of the lamina lucida in JEB due to mutations within the genes forming laminin 332; (d) Cleavage at the space between the sublamina densa and in the upper papillary dermis in DEB due to absence of COLVII.