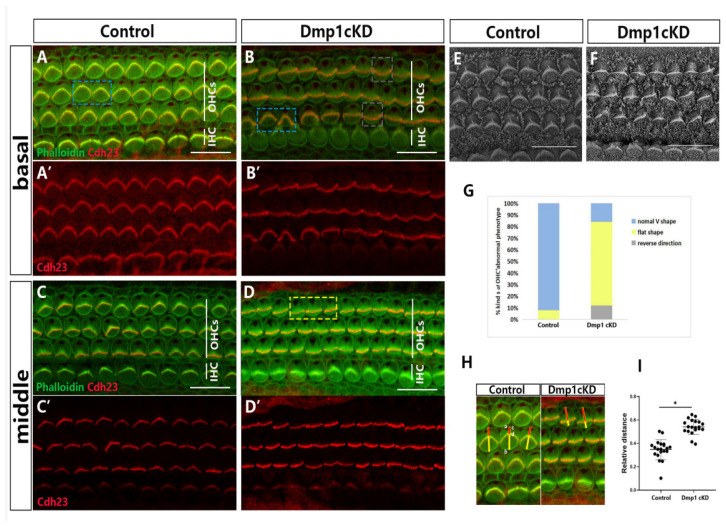
Figure 2.
Stereocilia hair bundles defected in Dmp1 cKD mice. (A–D): Whole-mount images of middle and basal turns of cochlea from control and Dmp1 cKD mice, Cdh23 staining of stereocilia junction protein was singly showed in (A′–D′). In the control cochlea (A,C), the stereocilia bundles were “V”-shaped and essentially symmetrical (blue bracket), while many hair cells’ stereocilia bundles had a defective shape such as a flat shape (yellow bracket) and reverse direction (grey bracket) in Dmp1 cKD cochlea (B,D). (E,F): SEM of hair cells from basal cochlear turns of Dmp1 cKD and control mice at P1. (G): Stacked bar chart of ratio of kinds of OHC hair bundles phenotype in knockdown and control mice (3 mice per group). (H,I): The amesiality of hair bundles in Dmp1 cKD mice. As shown in (H), the stereocilia bundles were globally moved toward one side (inner hair cells side) in single cells of Dmp1 cKD mice. It can be quantified by the ratio of cd/ab. ab (yellow line): the distance from the center of the blank area of the cuticular plate to the other side of the hair cell (close to the inner hair cell side). cd (red line): the center of the blank area to the V-shape vertex of hair bundles. Moreover, the result was shown as the cluster diagram in (I). Statistical significance was calculated using a t-test. * p < 0.05. Scale bars: 10 µm (A–D) and 5 µm (E,F).