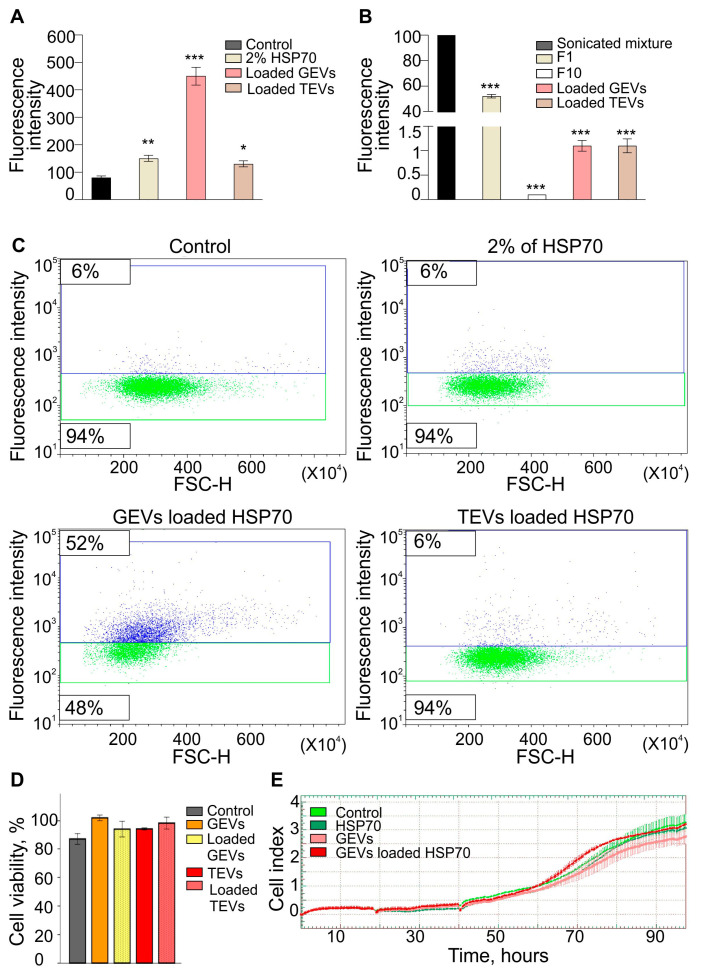
Figure 4.
Grapefruit exosome-like vesicles (GEVs) and tomato exosome-like vesicles (TEVs) mediated the delivery efficiency of exogenous HSP-70 proteins to human cells. (A) Fluorescence of Alexa Fluor 647 (AF647) labeled-HSP70 in the initial mixture and loaded samples of GEVs and TEVs, as well as washing filtrates (F1 and F10). After loading, excess free proteins were washed out, as shown from F1 to F10. Similar to TEVs, GEVs showed a loading efficiency of 1.10% when compared to the initial amount added to the vesicle suspension (sonicated mixture) (*** p < 0.001; One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, n = 3). (B) Fluorescence intensity of the uptake of GEVs and TEVs loaded with HSP70-AF647 by glioma (Gl-Tr) cells. (C) Delivery efficiency of protein to recipient cells by GEVs or TEVs analyzed by flow cytometry. Fluorescence signal accumulation into Gl-Tr cells was higher by loaded GEVs than the control (untreated cells) as well as 2% of free protein and TEVs (*** p < 0.001, ** p < 0.01, * p < 0.05; One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test, n = 3). (D) Cytotoxicity of grapefruit or tomato vesicles loaded with recombinant HSP70 for Gl-Tr glioma cells. The cytotoxic effects have been studied by the AlamarBlue cell viability assay after 48 h of incubation. No cytotoxic effect was determined when treatments were compared to untreated cells (Control) (p > 0.05; One-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post hoc test). (E) Cell index in real-time after treatment of Gl-Tr glioma cells with HSP70, GEVs, or GEVs loaded with HSP70. Control cells were incubated with culture medium only. The average of two replicates is shown for each condition. Error bars represent standard deviations.