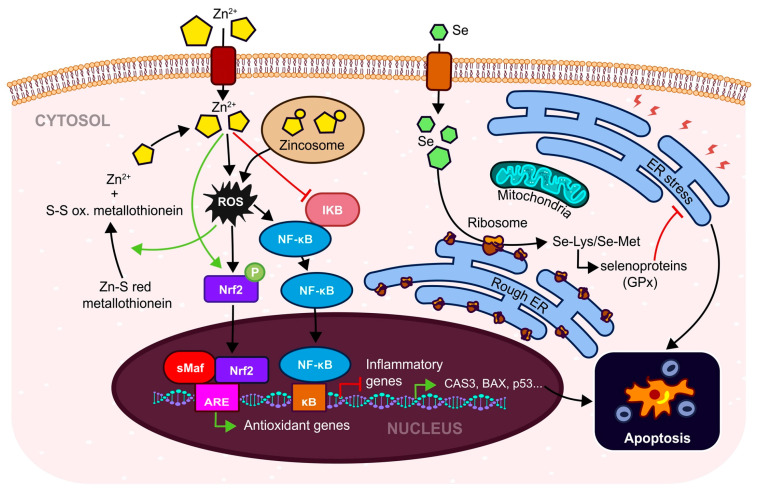
Figure 5.
The action mechanism of zinc and selenium in response to oxidative stress. Zinc can be released from metallothionein under protein reduction (formation of disulfidic bond after releasing zinc bound to sulfur in its oxidized form). Free zinc can act directly in reducing OS or can act via activation of Nrf2 signaling (green arrows) and can inhibit (red line) NF-κB signaling. On the other hand, selenium is incorporated in the amino acids lysine and methionine, and is used in the proteosynthesis of antioxidant enzymes and selenoproteins such as GPx which have the ability to reduce oxidative stress (red line).